What do you visualize when you think of a designer? Do you think that a designer is somebody who simply creates beautiful and elegant designs for its users?
But let me tell you that design is much more than just an artistic job. Along with creating pleasing designs, a successful designer also has to essentially understand the user’s psychology that can either create or break the user experience.
The users’ psychology enables the designer to build a very streamlined experience for its users that can improve the overall user experience design.
So, fortunately, there are various design psychology principles for designers that can help them with the necessary guidance towards creating a good user experience.
The significance of psychology in UX design
In today’s times, you will find that user-centered design is prioritized, and consequently, designers prefer to have a deep understanding of their target audience.
The book “The Design of Everyday Things” written by Donald A. Norman clearly specifies that design can be considered as an act of communication, i.e., where the designer needs to have a proper understanding of the person with whom he/she communicates.
This further helps designers to get a better idea about the fundamentals of human behavior, perception, motivations, and endeavors. Also, designers can skillfully apply psychology in the design process that will allow them to get a thorough understanding of their potential users’ preferences and needs.
Such a smart move of keeping psychology knowledge in mind while creating designs helps in producing designs that reach users’ expectations leading to greater purchase and maximizing business outcomes.
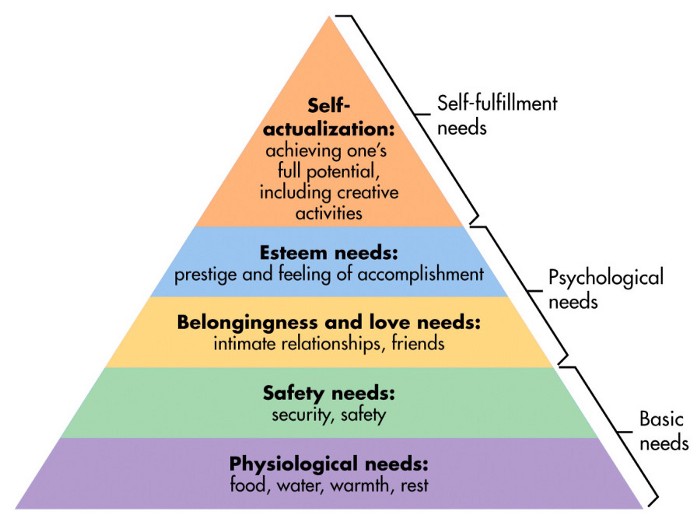
So, basically what I am here trying to make you understand is that UX design seems to have a long-term relationship with psychology. According to Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, just on top of our basic needs, we have psychological needs. All these make us desire, compete, collaborate, build and destroy.
Psychology principles empowering UX designers
In this section, I have assembled and simplified 13 psychological principles which will help you in enhancing the reliability, usability, and effectiveness of your creative designs.
Hick’s law
One of the main functions a designer has is to synthesize information and make things available in such a way that it doesn’t let the users feel overwhelmed at any point in time.
Now, this can be directly related to the very first basic principle: Hick’s Law. This particular law helps in predicting the fact that the time it takes in making a decision increases with the number and complication of options available.
Back in 1952, psychologists William Edmund Hick and Ray Hyman formulated this law after inspecting the relationship between the number of stimuli available and a person’s reaction time to any given stimulus. You will see that there is a real formula in order to represent this relationship: RT = a + b log2 (n).
Relax, you don’t need to understand or learn the math behind this particular formula to get a hold of what exactly it means. Here, the concept is very simple.
As discussed before, the concept is all about the time the users take to directly respond correlates to the number and complication of choices available.
Also, it reveals that complex interfaces end up resulting in longer processing time for users, which is again important since it can be seen as related to a primary theory in psychology named cognitive load.
Let us discuss one of the examples of Hick’s Law: remote controls. As you can see that the TV features have been increasing over the decades, so as the options that are available on their corresponding remotes.
Therefore, it resulted in complex remotes production that using them needed muscle memory from repeated use or an important amount of mental processing.
As a result, it led to a phenomenon named “grandparent-friendly remote.” So, by pressing off everything except for the necessary buttons, grandkids could easily enhance the usability of remotes for their family members.
Take a look below at the modified TV remotes which can simplify the “interface” for grandparents.

Gestalt Principles of Visual Perception
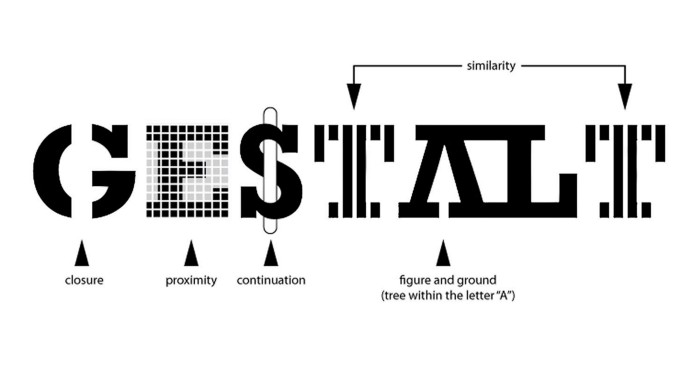
Gestalt is a psychological theory which is around 100 years old but still hasn’t lost its originality. Since the word, “gestalt” means “unified whole” therefore the theory examines users’ visual perception of elements in relation to one another.
That means it shows how people look after unifying the visual elements into groups. Also, the principles upon which users form the groups, consist:
- Similarity. If a user happens to see objects that look quite the same, they might automatically recognize them as the individual elements of one group. The similarity elements are generally defined with shape, size, color, value, or texture. And the similarity provides a sense of clarity between the design elements to the users.
- Continuation. According to this principle, the human eye naturally moves from one object to another. Usually, this happens via the creation of curved lines enabling the eye to flow with the line.
- Closure. This is a technique that is based on the human eye’s tendency to view closed shapes. Closure usually works where an object is incomplete yet the user recognizes it as a complete shape by simply filling in the missing parts.
- Proximity. While objects are kept in close proximity, the eye recognizes them as a group instead of considering them individually although if they aren’t alike.
- Figure/Ground. It is the principle that demonstrates the eye’s tendency in order to separate objects from their background. You will find many examples of pictures showing the two faces based on where your eye is fixed on the background or at the object.
Also, the Gestalt principles reveal that our brain looks for playing tricks with us, therefore, the designers need to be careful about that fact while creating processes in order to prevent the possibility of confusion or misunderstandings.
The Psychology of Persuasion
Since influencing others is a science of human behavior which can be utilized to enhance the success of your company. Therefore, users shall be convinced before taking steps on any sites. In order to maximize user satisfaction, the Psychology of Persuasion can be considered as one of the strongest approaches.
This law is derived from the famous book Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion written by Robert Cialdini where he has listed some of the principles such as Reciprocity, Authority, Scarcity, Liking and Social proof.
- Reciprocity
By offering something valuable beforehand to your users can make them feel indebted, and consequently, they might want to reciprocate to a certain level. So, providing free eBooks, podcasts, blog posts, or any other free content in return for the user’s email address can be a great example of reciprocity.

- Authority
This principle expresses that many of us think that we cannot be experts at everything. Therefore, we prefer obeying authoritative figures and experts of high status since they are considered to be very trustworthy. Authority is generally conveyed via titles (Dr., Prof., CEO), visual appearance, and also the success of a brand. High-status titles and academics help people to rely upon others by supposing that they have a comprehensive knowledge of the field.
Also, associations with successful organizations are usually mentioned to build a level of respect and credibility for the organization.

- Scarcity
People are seen valuing things that are either limited or are simply available for a limited time period. This principle triggers a psychological phenomenon named as FOMO, or “Fear of Missing Out”.
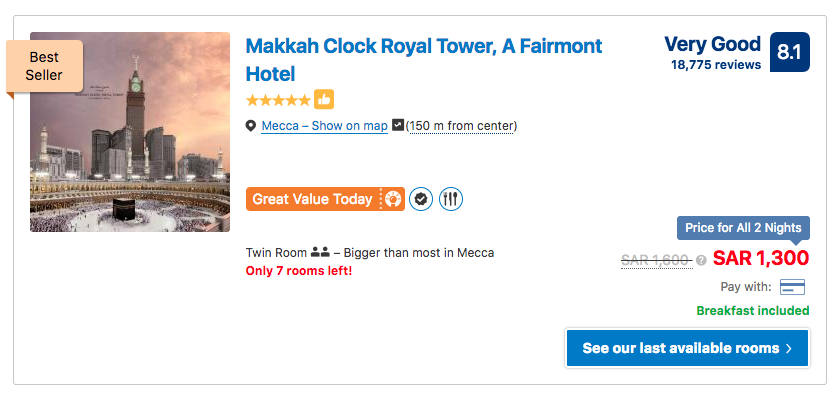
An example of this is used on Booking.com where visitors can see the rooms available, and make a decision before it gets late.
- Liking
It is quite obvious that you will agree to the requests made by the people you like. So, the big brands play it quite smart by using celebrities, models, and athletes to popularize their products and services. Companies are seen interacting with users via various channels of social media and blog posts to build a relatable feeling with the users, also enhancing the company reviews and ratings.

- Social proof
Sometimes we depend on others for guiding our behavior and deciding what’s good for us. We keep on seeking validation for our decisions, actions from experts, peers, or previous users. In e-commerce, websites tend to use social media proof like reviews, ratings, and suggestions to captivate users and assist them in making the right purchase decisions.
For example, there is a section in Amazon, “Customers Who Bought This Item Also Bought” in order to make items much more relatable to its users.

Memory Limitations
Memory can’t always be reliable. Basically, the way in which we store information can be again reconstructed by our feelings, beliefs, thoughts, and surrounding environment. Many of the studies reveal that people usually create false memories in which they might remember things that never took place or even remember things in a very different way.
As you know that memory is suggestive, therefore, it is very essential to create designs depending on the brain’s habit, or mental models, since they can be easily remembered.
Mental Models
Mental models are usually formed from an individual’s expectations and experiences of the physical world. People do have a mental model of interacting with objects or systems. Since the users spend a lot of time over the internet, they happen to form mental modes of interacting with and what to look for from interfaces.
So, if your product’s features and design do not match with your users’ mental models, then there is a possibility that the users might find it difficult to use your products.
In order to offer an effective online experience to your users, you will have to match their mental models in regards to easily using the products.
The Psychology of Colors
Color psychology can be considered as the science of how color affects human behavior. The ability to view color is a highly complicated process. Both the brain and eyes work together to translate what we see in colored pictures. Such a translation is subjectively associated with thoughts and feelings and is further utilized as a marketing mechanism in many industries.
Generally, users believe that color helps in increasing brand recognition. While selecting colors for your site and branding, you need to understand your target audience, timing, and purpose to improve the efficiency of your design. Let me tell you that positive feelings are connected to higher quality, which means your sales will possibly increase if your users like what they see.
In fact, people can overlook usability concerns due to pleasant aesthetics. Below are the general characteristics of color.
- Red. This color is generally associated with strong, passionate, or aggressive feelings. It represents both good and bad feelings that include love, passion, confidence, and anger.
- Orange. This is a warm and energetic color that brings feelings of excitement.
- Yellow. It is considered the color of happiness. This color symbolizes joy, warmth and sunlight.
- Green. It is the color of nature. This color brings renewing and calming feelings.
- Blue. This color generally symbolizes some corporate pictures. It represents calm feelings, but again it also relates to distance and sadness.
- Purple. This color represents spirituality, royalty, creativity, and imagination.
- Black. This color represents strength, authority, luxury, and sophistication.
- White. This color represents innocence, purity, clarity, and wholeness.
The Von Restorff Effect
This principle can also be named as the “Isolation Effect”. It says that distinctive items are more remembered than ordinary items. In order to be unique from the rest, your designs need to create a special experience for your users.
You need to be mindful of the fact that the Von Restorff principle shall be used in moderation. Trying to do everything at once can be really overwhelming for your users. Sometimes doing less can act in your favor.
Visceral Reactions

Have you ever been through a website that captivated your mind completely? Such a feeling can be considered as a visceral reaction. It is an instinctive response to a stimulus or experience that is created by chemical messengers in our brain. By eliciting visceral reactions via your design, you can let your visitors keep coming to your website. Also by receiving a visceral reaction from your users, you can generate a positive behavioral reaction in them that will further help you in getting their support and loyalty. This indeed helps in building a better image for your brand.
Dual-Coding Theory
This Dual Coding Theory was proposed by Paivio where he tried giving equal weight to both verbal and non-verbal processing. With this theory, your users can easily keep in mind the important things from your website by using the dual-coding system.
Memory has two definite yet interconnected systems, like one for verbal and the other for non-verbal information, according to the Dual Coding Theory. Your memory and learning get affected because of the relationship between these two channels.
Based on your experiences and understanding of the physical world, you tend to form visual images for the words in your mind. For example, if you are said to think about the word “tree” your brain automatically imagines green leaves, brown trunks, etc.
The Psychology of Shapes
The subconscious mind can be seen responding to shapes by connecting them to qualities that we consider they are representative of. These connections are formed from universal connections that are witnessed without being aware of it, just like the red octagon which is universally known to be the STOP sign. Brands prefer using shapes along with different colors to form their unique logos and some other visual elements to set off an emotional connection with their brand.
Fitts’ Law
This law suggests that the time taken to reach a target area is a function of the size of the target and distance to the target. It further recommends keeping target buttons nearer to expected mouse locations and even making them larger to reduce the interaction time. This particular concept is very significant in web design since the time needed to take the required action affects the conversation rates and also any additional time proves to be a risk of losing consumers.
Miller’s Law
Miller’s Law predicts that an average person can keep only 7 items (±2 more or less) in their working memory. It originated from a paper published in 1956 by cognitive psychologist George Miller. The psychologist discussed the limits of short-term memory and memory span.
The main concept behind this law is ‘chunking’ which regards collecting several bits of information into a cohesive gestalt. While being applied to design, chunking proves to be an important tool. It expresses the act of visually grouping related information into very small, clear units of information.
While we chunk content in design, we tend to make it simpler to process and comprehend. Users are able to easily scan the content and recognize what they are exactly interested in.
Jakob’s Law
Here comes the last principle: Jakob’s Law. This principle says that users spend the maximum of their time on other websites, and they would expect your website to be designed the same way as the other websites they already visited.
In the year 2000, usability expert Jakob Nielsen stated the likelihood for users to build up an expectation of design styles depending on their growing experience from other websites. The designers are encouraged to go for very common design patterns so that users’ confusion can be avoided, resulting in a higher cognitive load.
Learn more:
- UX in the age of personalisation
- Building user trust in UX design
- Ethical Design
- Getting familiar with cross cultural design
- Designing for sustaining attention
- User-centered design approach: Core principles & methods
- Humour in web design
- Cognitive accessibility in design
- Gender-inclusive web design
- Significance of writing for designers
- Complete guide to web design
Conclusion
By now you must have understood how psychology proves to be an efficient tool in design which enables in making the creative procedure much more productive, also prioritizing user-centered designs.
So, we have discussed some of the most useful principles for designers which can help them to understand their audience’s psychology and come up with great unique designs and patterns.
Now, it’s up to the designers how they would want to execute these principles in their design creation and connect with their users.
Subscribe
Related Blogs
UX Best Practices for Website Integrations

Website Integrations determine whether users stay engaged or abandon a site. I experienced this firsthand with a delivery…
How design thinking acts as a problem solving strategy?

The concept of design thinking is gaining popularity these days since people across different industries are using it as a…
10 major challenges that come across during an agile transformation

It’s no longer a mystery that agile was created as a response to the various concerns that the traditional waterfall…




