The visual or graphic of a website for any content found online is the first thing that grabs the users' attention. This is the very first moment of interaction - where the good design sustains it, and the bad one pushes the leads to oblivion. More about sustaining attention with good design here.
But what is it exactly that makes the user ponder over the content a bit more in one case, while he or she is repelled by the other design? What is this design doing right, that makes the user want to give it more of their time and attention?
Questions as subjective as this invite a plethora of subjective answers as well. And even then, in all of these subjective answers, the different elements of design would remain dynamic and would vary from person to person as well - leaving a single common denominator - establishing trust. That's right, no matter how attention grabbing or unique a design is, if it fails to establish the trust between the content and the user, the sustainability is short lived and the engagement will soon be done and dusted.
Elements that make or break trust
Noted American psychologist Julian Rotter defined trust as “…an expectancy held by an individual or group that the word, promise, verbal or written statement of another individual or group can be relied upon…”
It has been noted that out of the several reasons that customers have for trusting a brand, a lot of those are UX centric.
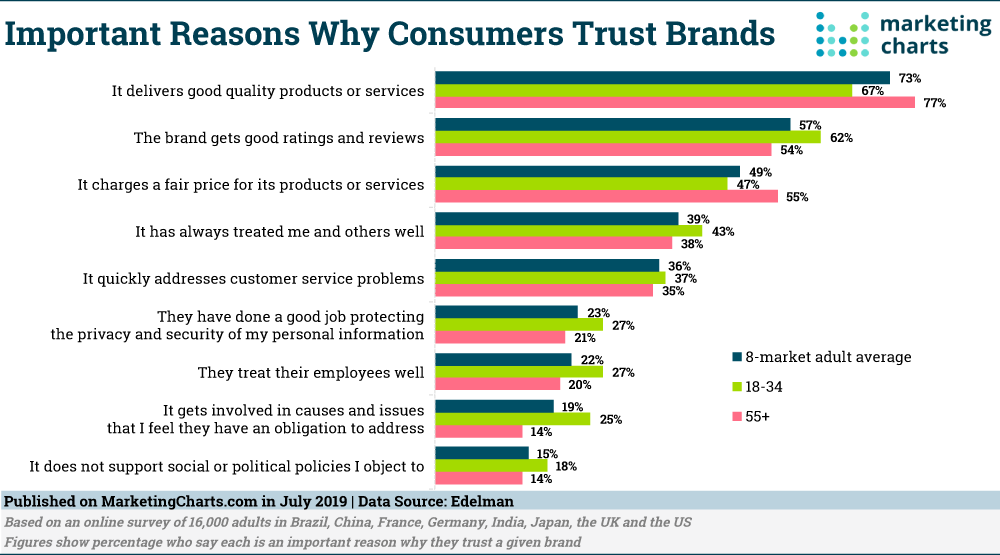
In the several elements that constitute design, some do the job of bridging the gap of reliance while some act as roadblocks in the same. Good design can be narrow down broadly to four obvious design elements
Brand definition
While some users may be concerned only with the end product, a majority of users will be interested in learning more about the brand that is providing them that product to eradicate any doubts and to finalise their purchase with a trustworthy vendor. Therefore a strong brand image is one of the first things that you should formulate in the form of a cone size but impactful About Us, preferably also envisioning your goals and mission. A well-planned design discovery process can be beneficial to define your brand. Read how.
Design Quality
There is a wide variety of things included when we talk of design quality. You may have to be familiar with cross-cultural design, you may have to consider design aspects for web accessibility, you may have to think about specifics of cognitive accessibility, you may have to plan for gender-inclusive design, you may have to understand an overall picture of ethical design, or you may just have to figure out how much humour can be incorporated in your design so that nobody gets offended by inappropriate elements. All the objects and elements of design are diverse and subjective to different users, but still there are some underlying principalities which suggest that a design is good quality.
- A well organised site that uses an appropriate colour scheme according to the theme of the product or service and related imagery is likely to be perceived better than an unorganized, uncoordinated site. For example, it would make sense for a startup selling plants to have green in their layout. Similarly, a cleaning services website that's cluttered would not leave a good impression on the user.
- Meaningful navigation labels indicate that the company considers the time of the users to be valuable and does not want them to lose their way in a complicated website. Labels that are too clever or unique might be good only if the user actually has the leisure to appreciate the minute details, otherwise they will just be stuck and will probably leave the site.
- The visuals of the website need to be designed giving the target audience in mind. When it comes to young adults, they consider flat designs more professional, leaning more towards minimalistic patterns. When it comes to older audiences, they would need something a little high and contrast as they are likely to have a poorer eyesight in comparison, hence low visibility colour themes like white and yellow would not be appropriate.
- Lastly, spelling mistakes, typos, broken links or outdated references greatly degrade the credibility of the website and communicate over all lack of attention by the owner. Most users are likely to be sceptical of every piece of information provided by a website once it has displayed an error in the content.
Upfront Disclosure
If there's one thing that's even worse than bad design quality, it is being secretive about information or using customer data in a different way then it is usually expected by the user to be used. Like in real life, even on the web people appreciate when websites are upfront with all the information relating to the customer experience especially if it includes details like terms and conditions to a specific product or service. It also includes details like prominently displayed contact information, stating any additional fees or charges for products, providing the links to return policy, guarantees and even revealing shipping charges before asking for the billing information of the user.
When all the information is upfront, it leads to a feeling of transparency and implies to the customer that the organisation is being honest to them. Therefore, every miniscule part of design has to be taken care of and every small decision matters. Learn more.
Correct and current
The content on a website related to Information about your business should exude class and precision. If your website provides services relating to a particular sector, be sure to include relevant information about that in your website as well as be mindful that all the data is correct and updated regularly. To include a more personal touch, pictures about your service would add value to your site. For example, again, if a website deals in plants, instead of showcasing just the plants they could also include pictures about their plantation methods, their teams, etc. Having a human touch greatly helps in establishing connections when the entire transaction is on the web.
Also keep in mind to include the full range of the products and services that are offered and not just a tiny bunch, as customers could perceive things differently and feel that their needs would not be addressed if they don't find their concern being listed clearly on the website. If the plant business shows pictures of only dealing with commercial clients and supplying ornamental plants to big organisations, individual consumers like you and me would feel left out and could even perceive that they do not cater to audiences like us.
External trust signals
How connected a website is to the rest of the web is directly indicative of how much they value and learn from market transactions and changing trends over time - in turn showcasing how invested they are in the user research that is undergone before launching a product or service. It is impossible to stay in vacuum in a world that is so intricately connected. Mentioning your partners or major clients on the website could help back up your credibility, even better if those partners or clients are known players in the industry and have credible websites for themselves too. Including customer testimonials and reviews is also a good way to express that you're a legitimate, trustworthy source. Learn more about how you can carry out user research even without any direct access to users to understand more about your consumers.
How to build trust through design?
Analysing consumer expectations
First it is important to understand what exactly are the ideas that the consumer places on the concept of trustworthiness. For most of its users, a company being trustworthy would be associated with morality, transparency about their products and services, and whether or not the information offered by them is correct and unbiased. The quality of your products and services also do the job of making the consumers feel confident in their choices. A strong security framework is also necessary for the users to feel that their data is protected and is in safe hands.
After a product has been launched, tools like Google Analytics can be used to analyse what the users are looking for. While this is predominantly used by marketers, Analytics can give designers a fair idea of the kind of audience they are designing for and show them the exact pathway undertaken to arrive at a certain piece of content - useful in UX for creating hypotheses and personas.
Creating mental models
While creating user personas, surface level research is not enough. When a user encounters a problem, they have their own way of solving it and have a mental image of how a certain solution would look like. While these mental models are highly diverse and are always subject to change due to constant evolution, they can be decoded by analysing the new products and technologies that are influencing the general mass mentality.
Creating the mental models of users the resources will cultivate the ability to understand their feelings and thinking processes, hence creating better personalized User experience which again is a powerful tool to gain the users' trust. Identifying these critical markers before commencement of the project would increase the chances of designing a trust building product. A diverse design team can yield innovative results. Read how.
Being transparent
Being upfront can yield surprising returns in terms of brand loyalty, as there aren't many players in the market that are open to disclose everything. Your users have the right to know how exactly your organisation intends to use the data and what type of data they are collecting.
Also while personalising content is practised widely now, it is also extremely important to provide an alternative perspective once in a while to avoid being associated with propaganda and polarising especially if the organisation deals in information sharing. When a certain consumer only sees what they want to see on your platform, they could either become repulsive to other opinions, or dismiss your channel altogether on the grounds of being biased.
Studies have even shown that people are ready to pay more for a website that offers complete transparency regarding everything that concerns the user. Any specifications regarding the product - for example, if it formulated only for a certain kind of weather, etc. should also be disclosed.
The correct information hierarchy
It is important to not take the users' attention for granted. Even if you have it for just one second, it should be optimally utilised. This can only be done if the most important pitch is placed at an attention grabbing position. Imagine attracting a customer's attention and then redirecting it towards something that added no value to convert the lead into a customer. Having some knowledge of writing can do work wonders for designers. Learn now.
Decluttered designs
No matter what the organisation offers and is about cluttered interfaces and prove to be major hindrances that falter the user's trust. If the information is too much and overwhelming, the user will take a lot of time to arrive at the point and will likely not even retain the information which was actually important. Be very careful about choosing the right colours to inculcate a positive attitude in the user towards your product. A simple example could be avoiding excessive usage of red as it is usually associated with the failed transactions, spam and danger.
Easy navigation
Websites are expected to behave a certain way - for instance, clicking on the logo takes you back to the homepage. Something as widely understood as this should not be altered with as it can create discomfort and disappointment. While building a site, things should be as obvious as possible as that is the underlying principle behind making something user-friendly. Users don't want to be lost in complex sitemaps and ghost buttons. A smooth User experience creates a feeling of similarity and friendliness
Usability
A UX designer should always keep usability on the top priority, far ahead of factors like uniqueness and trendiness. The importance of usability can be understood by a real life example - a store that looks outdated or dusty, or looks way too chic and inaccessible will spike discomfort in the consumers. The same goes for websites as well - if feelings of familiarity and friendliness are not arisen in the users while they use a website, they will likely experience discomfort and not want to associate with the product. They must always feel that the product is easy to use and simplistic in nature.
Good online copies
Content and design go hand in hand. Once you have attracted the attention of the user, stellar content will convert the lead to an actual customer. For the person on the other end to trust your online copy, there are a few pointers that you should keep in mind.
- Avoid usage of complex words that are easily replaceable by simpler ones.
- Avoid using intensifiers like very really or extremely that add no real value to the copy.
- It is wrong to assume anything - the text should better be talking about facts and figures.
- Do not refer to your end users as 'users' or 'customers' or 'clients'. The content is a method to establish a relationship with your users in the very first impression. Hence, calling them 'readers' or referring to them as their designations would appear more friendly.
Omnichannel consistency
To leave a long lasting impression on the users about your brand image so that they associate certain colours and symbols with your organisation, omni channel consistency must be maintained. This means not all of the various channels that deliver your presence online should post the same kinds of things and maintain a similar image. This ranges from your social medium to your website to the kind of engagement you practice within the community. Even the landing pages and display ads should be congruent with the overall theme of your brand.
The reciprocatory principle
A very simple way of gaining trust of the user while engaging with them is to give away something for free. Look at the whole transaction with a reciprocative point of view - when you give away something with a good intent, the consumer is more likely to engage with you further and begin trusting you with their information in return. If giving out on the entire piece of content is too much, address recommended to provide a brief summary of the content to the consumer before making them subscribe or even fill out a form.
Accountability
Consumers realise that sitting behind the screen is also a human and that there is scope for error - and they are ready to let it go as long as they see that the company holds its products and services accountable for where they lack. For example if your server is down or is under maintenance, just let them know! There is nothing worse than being shady and secretive about the product or service you're providing.
Testing prototypes
There must be thorough product testing before it is released to the actual market as design is very opinion based and subjective and it doesn't really require expertise to give suggestions on. Therefore, a large scale testing can be done by involving as many people as possible. Asking the users to fill out a form as feedback or even interviewing them would provide essential information to work upon. Having a design system at scale can help to a great extent. Read more.
Adding a personal touch
A very simple yet effective way of gaining the trust of users is by adding a more personal and human touch to your online profile. And how to do that? By letting the humans behind your systems shine. A separate page on your website that talks about your team, and includes pictures of your workspace and even the people involved will work immensely in your favour.
Another extremely common but highly effective way of creating a personal touch is by adding testimonials and reviews and a prominent part of your website. The reviews included should be genuine - because if all the testimonials are all positive these will again give rise to suspicion of ingenuine or paid feedback.
Engaging with your customers is also encouraged. As a business, when you have deduced the perfect channel that boasts of a good presence of your target audience, take the time to create posts that are more engagement centric - like asking questions or conducting polls - as these tell the user that you're ready to go the extra mile to listen to them.
If owing to all the positive aura reflected by your site, a customer does end up giving you their email address, do not spam them! If they see an email from you every morning, they are most likely to report you as spam or unsubscribe from the mailing list.
Site security display
All details regarding a site's security such as an SSL certificate should be prominently displayed to assure the user that any personal contact information or bill information that they provide is in safe and secure hands.
FAQ Section
An exhaustive FAQ section really simplifies the job of reaching out to the right kind of audience. It makes the consumer feel that the company has taken enough care to let the user make an informed decision for themselves instead of just asking them to buy it. It also makes it much easier for your customer support team as they are relieved of answering redundant questions.
Being easy to contact
Lastly, you want your customers to easily be able to reach out to you to provide you feedback or ask you questions. Once they feel that you are accessible and also proactively responsive, trust builds up to a significant level. Make sure to display all contact information like contact numbers or emails and keep updating those regularly.
For a complete guide on web design, read here. And to know how to perform website redesign the right way, read here.
Conclusion
If your website checks all these boxes, the UX is definitely trustworthy. In the longer run, only sustained relationships bear fruit even throughout testing times - hence gaining the user's trust should not be taken lightly and appropriate measures should be taken to achieve it.
Subscribe
Related Blogs
UX Best Practices for Website Integrations

Website Integrations determine whether users stay engaged or abandon a site. I experienced this firsthand with a delivery…
How design thinking acts as a problem solving strategy?

The concept of design thinking is gaining popularity these days since people across different industries are using it as a…
10 major challenges that come across during an agile transformation

It’s no longer a mystery that agile was created as a response to the various concerns that the traditional waterfall…




