The concept of design thinking is gaining popularity these days since people across different industries are using it as a strong problem-solving strategy.
The design thinking method proves to be beneficial in the process of growth and innovation in any business, and therefore, you should be prioritizing it in your organization and get the most out of it.
So, today in my article let’s find out what exactly is design thinking, how it can help, and lots more.
Design Thinking: A non-linear process
If you think design thinking is for only designers then let me tell you it isn’t so. It is for everyone like freelancers, creative employees, and leaders who look forward to infusing design thinking into each and every level of a company, product, or service to drive new alternatives for society and business.
So, the design thinking process at its core is basically all about user-centered design. This process tends to revolve around developing a proper understanding of the people for whom you’re designing the services and products.
You’ll find that some of the world’s leading brands like Google, Apple, GE, and Samsung have quickly adopted the Design Thinking approach, and this process is also being taught at some leading universities around the globe including Harvard, Stanford, and MIT.
Cycle of design thinking
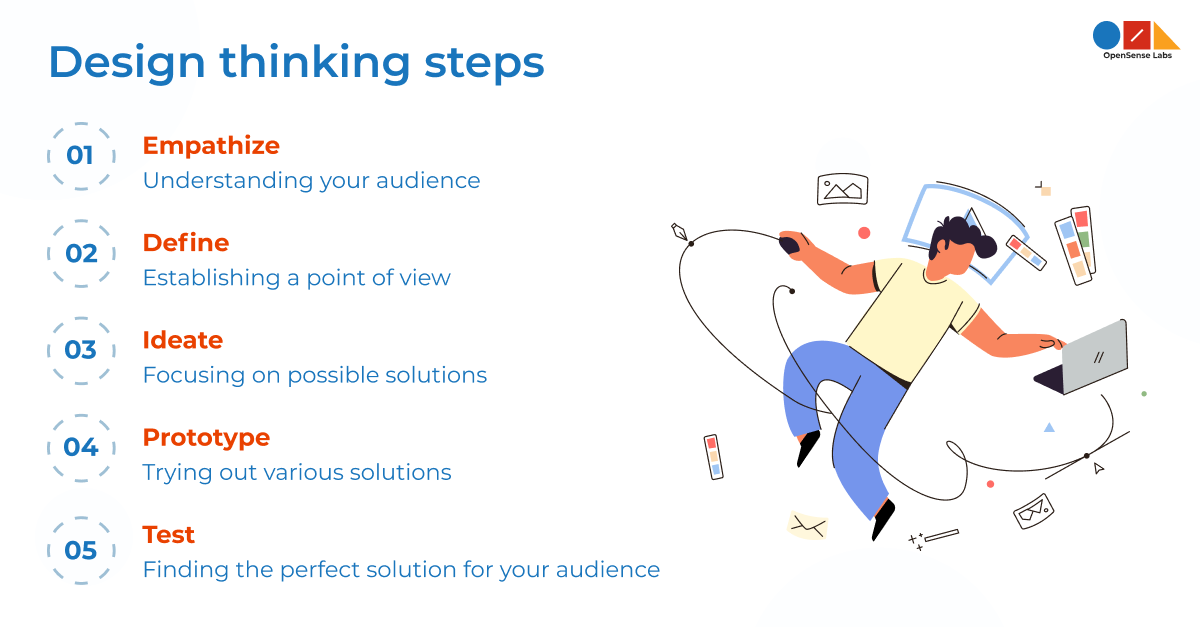
The design thinking process comprises five steps. You can consider these steps as a part of a cycle that keeps moving around and around till a proper solution is found.
Empathize: Understanding your audience
The very first step in the cycle is to empathize. Empathy is critical to the rest of the process since it is how designers get an opportunity to learn about their users. So, here the point is when you empathize with someone, you tend to see the world through their eyes.
When it comes to designers, empathy is simply about putting aside their own predetermined ideas to properly understand the concern from the point of view of the user. Basically, the goal is to recognize the user’s thoughts and inspirations beyond gathering quantitative data.
Define: Establishing a point of view
Next during the Define stage, you happen to put together all the information you have created and collected during the Empathize stage. This is exactly the stage where you can analyze your observations and synthesize them to define the primary problems which you and your team recognize.
Also, the designers in your team can gather awesome ideas in order to establish functions, features, and any other elements which enable them to resolve the concerns or, at least, enable users to solve problems on their own with the least difficulty.
Moreover, it is very important to define the problem statement in a human-centered manner.
Ideate: Focusing on possible solutions
The next stage can be considered as ideate. Ideation is simply about creativity. So, the fact is rather than ideating alone, it is convenient to just bounce concepts around with a group of people also committed to solving the issue.
Also, bringing ideas into a group setting enables them to transform and grow into a robust solution.
In this ideate stage, all ideas are great ideas. Here, you’re not restricted to the rules of logic or execution. In fact, you’ll not know what idea might just lead to the perfect solution for your users.
And, I mean it's quite obvious that having a diverse group of ideators is very significant and people from different careers, backgrounds will certainly come with a wide range of solutions.
Prototype: Trying out various solutions
Once the ideas are out then it’s time to prototype. Prototyping enables designers to preview the practicality of a solution in regards to implementation by creating a scaled-down and reasonable version.
Well, a prototype is considered valuable since it can reveal flaws and weaknesses in your design. So, when flaws are found, you can possibly return to a previous step in the cycle.
The design thinking process is mainly non-linear and flexible. And it’s really a good thing if you can flexibly move to any of the steps of the cycle whenever necessary.
Exactly knowing when to return and re-evaluate the problem definition is very important, and your resulting design will surely be better for it.
Also, once you settle on one or more prototypes, you can possibly take time to look for what your users think.
Test: Finding the perfect solution for your audience
Finally, the last step is the test. You need to bring your design to the users and collect feedback since it’s possible that you will be heading back to the ideation stage a few more times before you reach a final solution. Well, there are several ways to test.
Let me tell you here about two of the most popular methods: 1) allowing your user to experience the solution without any explanation from you 2) letting them take you through their experience and even asking them questions to make them think further about their experience.
Once they complete their trial, you can possibly ask them some follow-up questions. Then you can look after any weak spots and let the user elaborate.
And, lastly, observe. Watch out whether they are using the product as intended or not.
After testing, you need to gather your data, and if in case the solution needs to be fixed, you can move backward to repeat a previous step. Let me here tell you, the solution is never perfect on the first attempt. So, just be patient.
Design thinking as a problem-solving strategy
Design thinking is regarded as a creative problem-solving strategy that is designed to put you into the minds of the users you're solving concerns for. The below points can justify this very statement of design thinking as a problem-solving strategy.
Giving rise to other strategic innovation
Very sadly, humans are not capable of imagining things they believe aren’t possible, also making it hard to create something that simply doesn’t exist. Even so, design thinking enables strategic innovation that leads to amazingly creative inventions and solutions.
Basically, it brings out the man’s creativity and capability to think "out of the box" in regards to what is possible.
Solving vague or hard to define concerns
Generally, it is observed that consumers really do not know what exactly the problem is, still they know the issue and the fact that something is there to be solved.
Although, due to careful observation, a team that is well-experienced in design thinking can recognize the issue and develop a solution based on a consumer’s behavior.
Solving consumer pain points
Since the focus of design thinking is all about being observational and human-centric, very often many teams tend to uncover particular problems to which the consumers were not aware of or also given a second thought.
The process of design thinking provides convenient solutions to these pain points while they come up.
Helping organizations to run faster and efficiently
On the contrary to the traditional linear approach of problem-solving, which involves researching a problem for a very long time even without coming up with an outcome, the design thinking process can create prototypes and then test to observe how effective they are.
This type of iterative style is much more creative, customer-centric, and eventually gives a quicker result.
Focusing on collaboration
Even though the main focus on design thinking is to help end-users, they still encourage everyone to reach such solutions by working together. While you take a design thinking approach to problem-solving, many unique diverse ideas and perspectives can be introduced among us.
With more minds getting involved can lead to better innovation. The design thinking process gives an opportunity to employees to work with people outside of their departments.
For example, for a design thinking workshop if you bring different departments together, it can add new ideas and perspectives to the concern you’re trying to resolve and can even help in building relationships across teams.
Embracing ideation
"I thought that ____ might have been a great idea when we were still in the planning stages, but I wasn’t sure how to bring it up."
"I wasn't sure how people would respond to _____ so I thought to stay quiet."
So, tell me how many times have you really heard phrases like that in post-project meetings? Well at times the real challenge to innovation is not about a lack of support from management.
But it can be your own employees who could doubt themselves and may not be confident enough to share their ideas.
Therefore, design thinking can be considered as an iterative process that can help your employees feel more comfortable with expressing ideas.
Creating actionable solutions
Rather than simply talking about proper solutions to problems, design thinking tends to challenge you to make something beneficial from your thoughts. Like the prototype and testing phases enable you to observe how your potential solutions can work in real life.
You just don’t have to spend months of employee time and company money in order to identify if a concept really will work or not.
In fact, a simple design thinking workshop will be able to test the feasibility of your solution in just a day or two.
Implementing design thinking into your business
If you’re thinking of implementing design thinking into your business, then you can certainly start off with the below easy tips.
Embracing fluidity
We have already discussed that most of the design approaches comprise 5 phases, yet the process doesn’t really have to follow a particular order. You might find that starting off in the prototype or testing phase allows you to create better ideas.
Also, ideating first can help you in finding better empathy for your end-users. So, you don’t have to think that everything needs to happen in a specific order.
All you need is a sufficient amount of attention to every phase and not get worried about just following a set order.
Avoiding silos
Just remember that you’re not supposed to make the mistake of experimenting with design thinking on a department level. Like, if you think that only the development department or design team is where you’ll be starting first, then you already tend to forget one of the major tenants of design thinking.
So, it isn’t necessary that different ideas from people in the same department might simply produce as many innovative ideas as you’d love.
Therefore, regardless of how you start experimenting with design thinking at work, just do not fail to involve people across different departments and disciplines.
Finding your cheerleaders
If you’re looking to succeed in pivoting to a design thinking environment, then you’ll have to find people who will champion your cause. So, the people that look forward to this way of thinking will definitely be doing their level best to apply the perfect principles during meetings and projects.
You can possibly talk to them about the most convenient way to get other team members involved.
Also, never step back from encouraging them to reach out to employees and discover ways to bring more design thinking ideologies to their team.
Starting small
One of the simplest ways to sabotage yourself while you're bringing design thinking to the workplace is to begin too big. You shouldn’t be asking your team to find a way to entirely revamp your company with design thinking.
It is very convenient to go for small ways to introduce big concepts. Just holding a small brainstorming session with volunteers can be a good way to start small and find your cheerleaders.
Design Thinking: Case Studies
Most of the companies have turned to the design thinking process in order to create an innovative, and customer-focused culture.
So, in the below case studies, you’ll get to see how some of the popular organizations and businesses have adopted design thinking for achieving bigger things.
PepsiCo
In the year 2012, PepsiCo happened to hire its first chief design officer and CEO Indra Nooyi. In an interview Nooyi said, “now ‘design’ has a voice in nearly every important decision that the company makes.”
So, how did this corporate giant utilize design thinking as part of a strategy in order to turn around its declining market position, also driving growth?
Well, according to Nooyi, what happened was a shift in the company focus, from product design to consumer experience design. They began paying attention to how consumers communicate with the brand and to the overall user experience.
Therefore, you’ll find that today, design and the user experience are considered an essential part of PepsiCo’s strategy, and it’s all attributed to design thinking.
Ericsson’s Innova System
Ericsson is a global telecommunications company whose networks successfully handle an estimated 40% of mobile traffic globally. It’s basically a big business with a large workforce, and it’s able to manage the problem-solving brainpower of the entire company with its design thinking platform, Innova.
So, Innova was set up in order to bring up innovation amongst Ericsson’s employees. Basically, it’s an internal program that acts as a startup incubator for ideas.
In an interview with Innova’s head of strategy and operational development for northeast Asia, Erik Chang it was revealed that Innova has 6,000 users who have submitted 4,000 ideas for new products.
And around 500 ideas have received funding, and five have been developed into actual products.
Since the ideas are coming from various different sources, Innova’s application of design thinking happens to skip the Empathize stage, and the Ideate stage is spread out on an individual level.
Even though it’s not a “classic” application of the design thinking process, the Innova system tends to emphasize employees’ creative potential and aims at a collaborative procedure in order to build profitable new ideas.
Samsung
Before becoming a design-focused brand, Samsung majorly manufactured inexpensive and imitation electronics for other companies. Products were developed and made by engineers in accordance with price and performance indicators and designers only came on board at the end of the manufacturing life cycle in order to make the products look consumer-friendly.
In 1996, the chairman of Samsung Group, Lee Kun-Hee decided that in order to be known for its innovation, it had to make design a priority and take it forward in the life cycle.
At this point in time, not even a decade later, Samsung is considered one of the biggest technology brands in the world, employing more than 1,600 designers who have helped the company win a number of design awards.
Read this comprehensive guide to web design to know more.
Conclusion
I hope now you’re quite familiar with the design thinking process and how it proves to be a problem-solving strategy for your business. Now it is your call to adopt this process and drive growth and innovation at your organization.
So, without waiting any longer just make design thinking a priority and achieve greater success.
Subscribe
Related Blogs
UX Best Practices for Website Integrations

Website Integrations determine whether users stay engaged or abandon a site. I experienced this firsthand with a delivery…
10 major challenges that come across during an agile transformation

It’s no longer a mystery that agile was created as a response to the various concerns that the traditional waterfall…
Design as a team: An extensive guide to cross-functional collaboration

Cross-functional collaboration plays a vital role in accelerating the delivery of better results for consumers. It promotes…




