Drupal's Role as an MCP Server: A Practical Guide for Developers
"The MCP provides a universal open standard that allows AI models to access real-world data sources securely without custom, fragmented integrations. By acting as an MCP server, Drupal becomes more than a CMS, serving as an intelligent layer that lets external LLMs interact with its content and tools through protocols and secure authentication."
As AI assistants improve, most advances have focused on model intelligence, while access to real-world data remains fragmented and hard to scale. Data is often locked in silos, requiring custom integrations for every new source. MCP solves this by introducing a universal, open standard that connects AI systems to data through a single, secure, and consistent protocol.
These ideas gained significant attention at the Drupal AI Summit, where the community explored how Drupal can act as an MCP server, allowing external large language models to securely interact with CMS data using standardized tools and JSON-RPC.
The discussions highlighted Drupal’s growing role as a reliable integration layer between AI systems and real-world content.
How the Drupal AI Summit Shaped Future Architecture?
During the Drupal AI Summit, the conversation shifted from broad concepts to practical architectures for AI integration.
Drupal is transforming into an orchestration layer that effectively connects content, data, and intelligence.
Alex Moreno from Pantheon discussed how Drupal’s modular design positions it as a bridge between content platforms and intelligent applications, making it easier to adapt as AI capabilities.
Continuing this discussion, Giorgi Jibladze from Omedia demonstrated how Drupal is functioning as a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server, integrating with tools like ChatGPT to improve user experiences with interactivity and context-awareness.
A key takeaway from the Summit was how well Drupal can present content, tools, and workflows to external llms in a structured and secure manner.
By utilizing configuration-driven tools, JSON-RPC communication, and OAuth 2.1 authentication, Drupal evolves from merely being a content repository to an active player in AI-driven workflows.
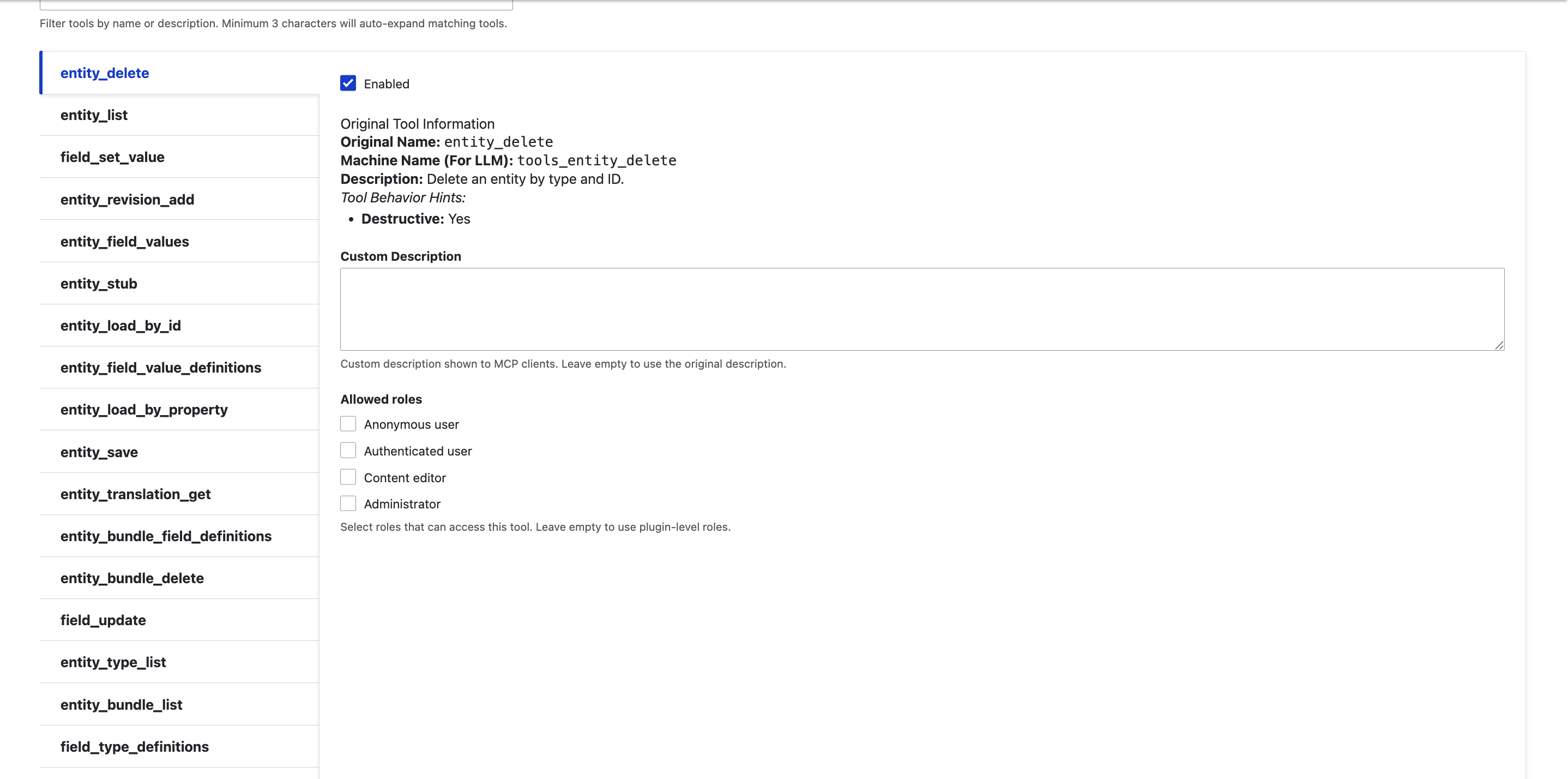
This is made possible through Drupal’s Tool API, which allows Drupal features to be presented as MCP-compatible tools, enabling AI systems to engage with Drupal in a consistent and controlled way.
- MCP Tool Configuration List: The admin interface located at /admin/config/services/mcp-server/tools offers a full view of the configured MCP tools, which includes their status, Tool API source, and authentication settings.
- Tool Configuration Form: Configuration form featuring Tool API autocomplete, options for selecting authentication mode, and settings for OAuth scope.
- MCP Inspector Integration: Testing MCP tools with the official MCP Inspector (npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector).
What is an MCP Server?
An MCP server implements the Model Context Protocol to expose data and functionality in a structured way, allowing any applications to extend their context using local and remote sources.
Drupal is well-suited to act as an MCP server thanks to its robust content management, modular architecture, and integration capabilities, enabling content to be exposed as resources and features as AI tools.
The MCP Server module brings full MCP compliance to Drupal, turning any site into an MCP-capable endpoint once installed.
Built on the Tool API module, it provides a configuration-driven way to expose Drupal functionality, with the included tool_ai_connector enabling immediate AI function calling with minimal setup.
How to Setup MCP Server?
The MCP module is Drupal’s implementation of the Model Context Protocol, enabling Drupal to function as an MCP server.
Here's how to set up and configure the MCP module for your Drupal website.
Step 1: Install and Enable the MCP Module
ddev composer require 'drupal/mcp:^1.0'
ddev drush en mcp –y
After enabling the MCP module, plugins must be enabled to define which Drupal features are exposed as MCP tools for AI assistants.
Step 2: Enable Plugins
The MCP module operates on a plugin-based system that allows developers to enhance its features. The main module manages the MCP protocol and acts as a base, while the specific actions and resources available externally are determined by plugins.
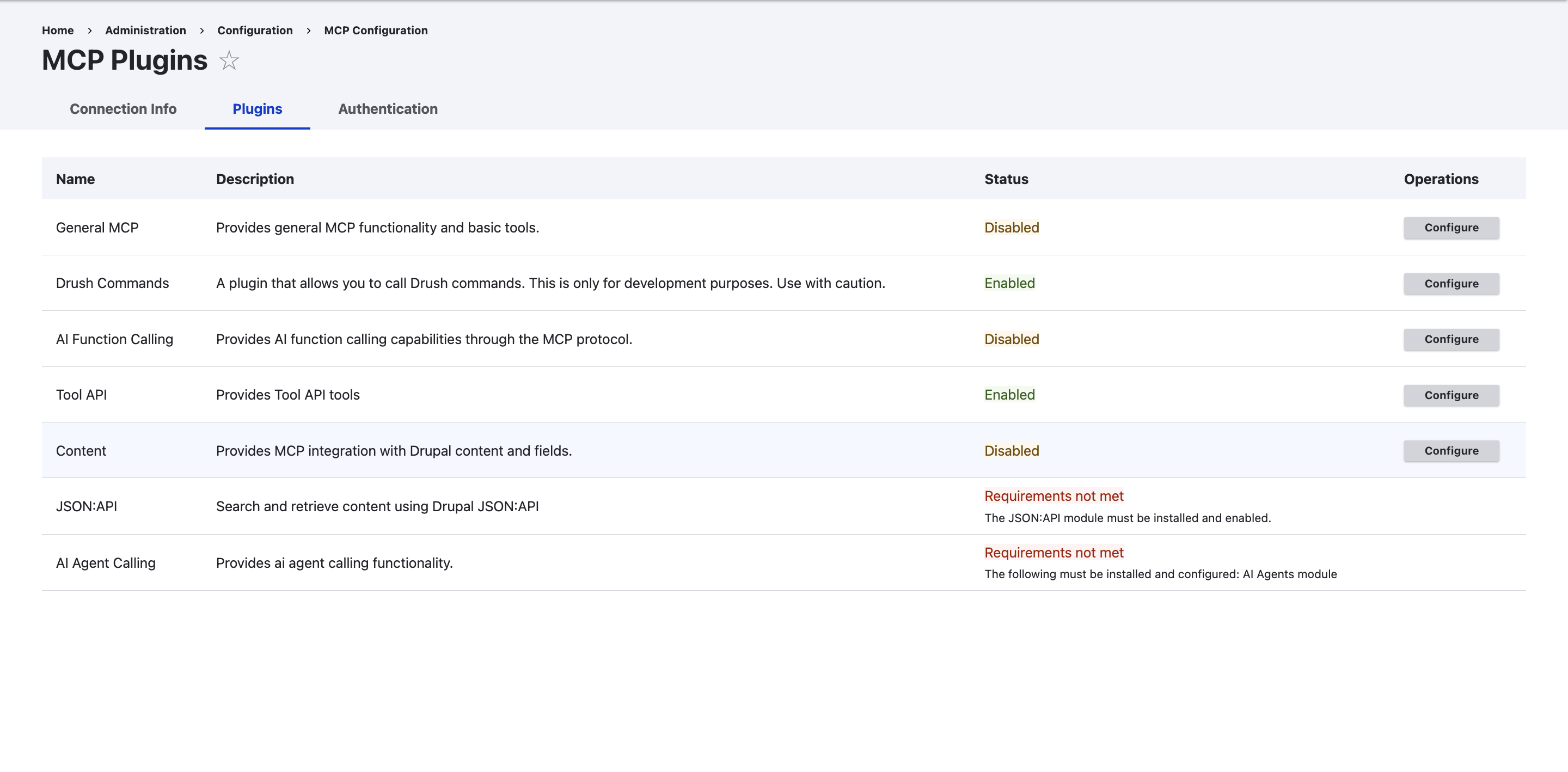
You can enhance MCP functionality in various ways:
- Utilize the optional submodules that come with MCP (explained below)
- Install plugins contributed by the community
- Develop your own custom plugin
Step 3: Optional Submodules
MCP includes two optional submodules that offer helpful plugins:
- mcp_extra - This exposes AI module function call actions, enabling MCP clients to utilize Drupal’s AI features.
- mcp_dev_tools - This allows controlled access to Drush commands via the MCP interface.
These submodules can be activated separately as per the requirements:
# Enable AI agents functionality
ddev drush en mcp_extra
# Enable developer tools
ddev drush en mcp_dev_tools
Note: to allow mcp_extra to show AI function actions, you must install and activate the Drupal AI module.
Set Up
Once you have installed it, you will see the MCP configuration form located under Web Services at /admin/config/mcp.
In this section, you can:
- Activate authentication (either token-based or using credentials)
- Turn on/off the plugins mentioned above
- Adjust settings for each plugin separately
- Choose which content types to make available (default is opt-in)
- Set user permissions for accessing MCP
Security Settings
Beginning with version 1.1, MCP offers improved security features:
- Permissions: Users need the "Use MCP server" permission to access MCP.
- Content Types: By default, content types are now opt-in for enhanced security.
- Authentication: Token authentication can be set up to use a designated user account rather than defaulting to UID 1.
- Command Restrictions: The mcp_dev_tools module allows for limiting permitted Drush commands.
What are the Types of Authentications Provided by the MCP Server and Role-Based Access?
The choice of authentication method for an MCP server depends on factors such as deployment size, environment, and operational sensitivity. Each method governs how clients securely authenticate before accessing MCP resources.
- OAuth 2.1 (Standard Recommendation): This is the main method for remote MCP servers. It employs authorization of code flows with PKCE (Proof Key Code Exchange) to ensure secure interactions, usually requiring user consent through a browser.
- API Key Authentication: Clients provide a pre-issued static API key in the request header. This method is straightforward for internal teams but is mainly suggested for prototypes or internal tools.
- JWT-Based Authentication: The server checks JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for stateless, signed, and time-limited access.
- Mutual TLS (mTLS): Both the client and server share digital certificates, offering a high level of cryptographic security.
- Basic OAuth: Uses standard OAuth access tokens without PKCE, offering more security than API keys but best suited for controlled or legacy environments.
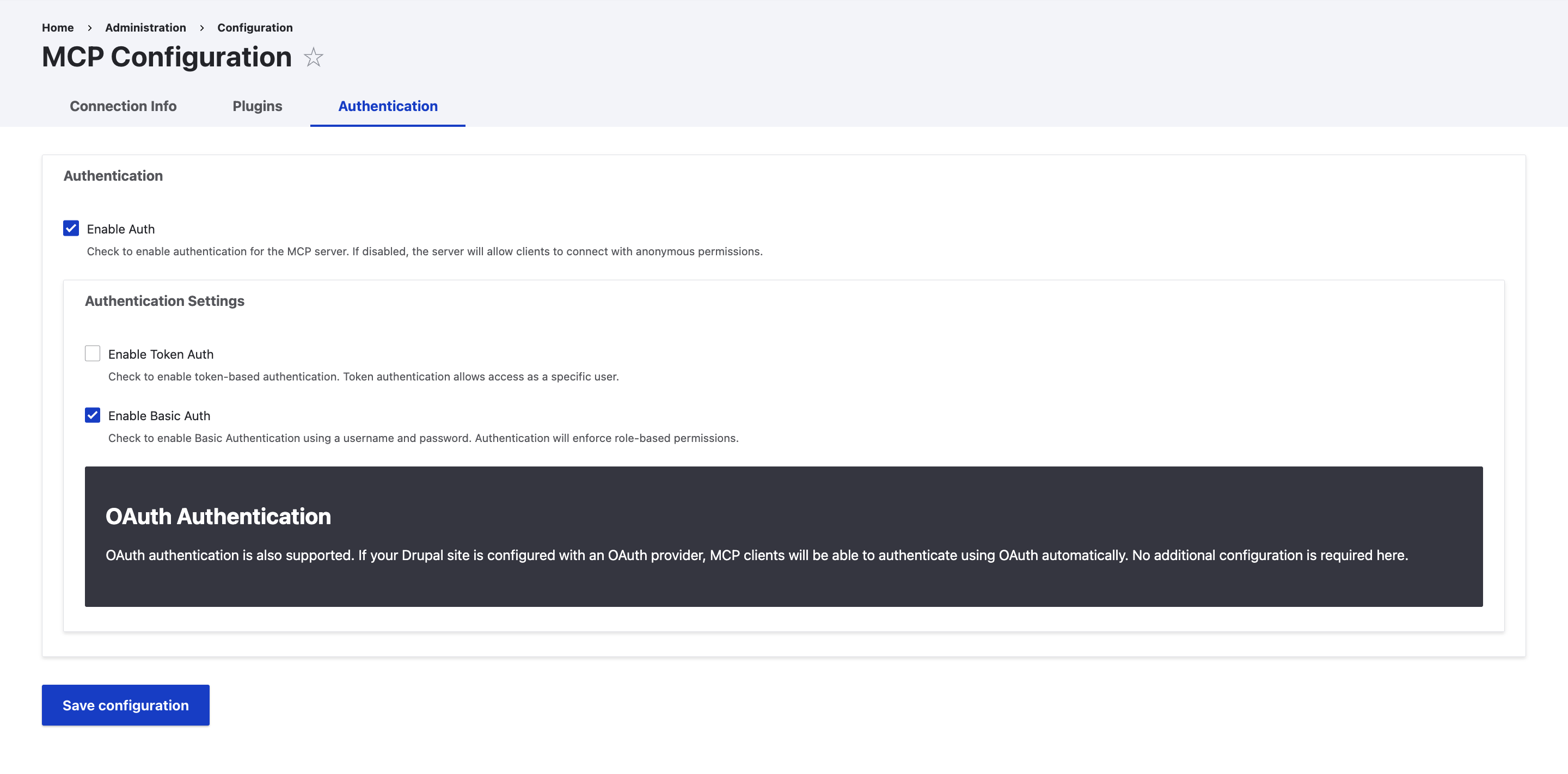
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in MCP
Authorization in MCP guarantees that after a client is authenticated, it can only execute permitted actions. RBAC plays a crucial role in this:
- Tool-Level Granularity: RBAC enables the assignment of specific permissions (like read:tools, write:tools) to roles, managing access at the individual tool level instead of the whole server.
- Typical Role Hierarchy: Roles are linked to permissions, usually including:
- Admin: Complete access to all tools and settings.
- Developer/User: Access to certain tools for task execution.
- Read-only: Can view tool outputs but cannot execute or alter tools.
- Dynamic Decision Making: MCP servers utilize the authentication context, such as role claims or scope within a JWT, to make immediate decisions on whether to allow, deny, or restrict tool usage.
- Context-Based Access: In more complex situations, access can be customized based on the specific context of the request (like user, data sensitivity, or environment), rather than solely on the user’s fixed role.
How to Use Drupal's MCP Server Via STDIO and HTTP?
Drupal supports two transport methods because AI integrations don’t all run in the same environment. Some run locally, some remotely, some in production, some during development.
The STDIO transport is best suited for local, controlled, and developer-focused workflows, while the HTTP transport is designed for remote, production-ready, and scalable AI integrations.
STDIO (Claude Desktop setup)
To connect Claude Desktop, add the MCP server config to the claude_desktop_config.json file. This file is located at:
- macOS: ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
- Windows: %APPDATA%/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
You can view and edit it from the Claude Desktop settings as well.
Insert the config object into that file and modify the credentials.
{
"mcpServers": {
"mcp-server-drupal": {
"command": "docker",
"args": [
"run",
"-i",
"--rm",
"-e",
"DRUPAL_AUTH_USER",
"-e",
"DRUPAL_AUTH_PASSWORD",
"--network=host",
"ghcr.io/omedia/mcp-server-drupal:latest",
"--drupal-url=https://mysite.ddev.site",
"--unsafe-net"
],
"env": {
"DRUPAL_AUTH_USER": "mcp_user",
"DRUPAL_AUTH_PASSWORD": "secure_password_here"
}
}
},
"globalShortcut": ""
}
This configuration tells the MCP client (for example, Claude Desktop) how to start and connect to a Drupal-based MCP server using Docker.
- mcpServers defines the list of available MCP servers.
- mcp-server-drupal is the identifier used by the client to reference this Drupal MCP server.
- command: "docker" instructs the client to run the MCP server inside a Docker container rather than directly on the host system.
- args specify how the container should be started:
- run -i --rm runs the container interactively and removes it when stopped.
- -e DRUPAL_AUTH_USER and -e DRUPAL_AUTH_PASSWORD pass authentication variables into the container.
- --network=host allows the container to access the local Drupal site directly.
- ghcr.io/omedia/mcp-server-drupal:latest. is the official Drupal MCP server image.
- --drupal-url points to the Drupal site acting as the MCP server.
- --unsafe-net enables network access required for MCP communication.
- env defines the actual credentials used by the MCP server to authenticate against Drupal.
- globalShortcut is optional and left empty here.
In short, this setup runs Drupal’s MCP server in a Docker container, securely authenticates with Drupal, and exposes it to the MCP client for local AI-driven workflows.
And once the file is saved, restart Claude Desktop. You will find your Drupal MCP server in the servers list, along with the count of tools (actions) it provides. If that number is visible, you are all set.
MCP servers use JSON-RPC as their communication layer to exchange requests and responses between clients and servers. In Drupal, this provides a standardized and language-agnostic way for MCP clients to interact with exposed tools and resources.
Conclusion
Drupal’s MCP Server allows developers to expose Drupal content and tools directly to AI assistants in a secure, standardized way. Instead of building custom integrations, developers can use MCP to let AI query content, trigger actions, or interact with workflows using familiar Drupal APIs.
This makes it easier to connect AI systems to Drupal in a standardized way, allowing them to discover, invoke, and interact with Drupal’s tools and resources without tightly coupling to backend implementations. MCP works across both local development and production environments, enabling teams to experiment locally and scale securely.
By acting as an MCP Server, Drupal becomes a controlled interface for external models and agents, exposing tools and capabilities based on defined permissions. This keeps Drupal flexible, secure, and interoperable while letting developers integrate intelligent systems without redesigning their architecture.
OpenSense Labs can help you design, configure, and deploy Drupal MCP Servers that securely connect your content and tools with AI systems without overcomplicating your architecture.
Subscribe
Related Blogs
What’s New in Drupal CMS 2.0: A Complete Overview

"Drupal CMS 2.0 marks a significant change in the construction of Drupal websites, integrating visual site building, AI…
Drupal AI Ecosystem Part 6: ECA Module & Its Integration with AI
Modern Drupal sites demand automation, consistency, and predictable workflows. With Drupal’s ECA module, these capabilities…
Inside the Drupal AI Summit: Themes, Speaker and What To Expect

“ The web is changing fast, and AI is rewriting the rules. It writes content, builds pages, and answers questions directly,…




