Imagine constructing a house without a blueprint or a set of plans.
It will be challenging to estimate the cost and labor required to construct. This can result in cost overruns and delays in the construction process. In addition, the absence of a blueprint can make it difficult to ensure that the house is constructed according to the owner's vision and specifications, leading to potential design flaws and mistakes.
Lack of planning can also result in regulatory and safety issues that may require costly and time-consuming modifications or even demolitions.
In other words, it would be chaotic, time-consuming, costly, and most likely a below-standard house that fails to meet the needs and expectations of the homeowner.
Similarly, developing a product without following a structured approach can result in a suboptimal product that fails to meet customer needs.
This is where Product Engineering Life Cycle comes in. It is a well-defined process that guides businesses in the development of new products, from the initial idea to the final product launch.
In this blog post, we will explore the various stages involved in the product engineering life cycle and the factors that can affect its length and complexity. We will also discuss some best practices for ensuring a successful product engineering life cycle, such as collaboration, early testing, and continuous improvement.
This blog will provide you with valuable insights and practical tips to help navigate the product engineering life cycle and achieve your goals.
Product Engineering Lifecycle
Product engineering is a complex and multi-stage process that involves designing, developing, testing, manufacturing, and maintaining a product from its inception to its end of life. Understanding the product engineering life cycle is crucial for businesses and individuals who want to bring their innovative ideas to life and achieve success in the market.
The product engineering life cycle typically involves several stages, each of which serves a unique purpose in bringing a product to market. The first stage is conceptualization, where the idea for the product is generated and its potential market value is assessed. This stage involves conducting market research, identifying customer needs and preferences, and exploring various design options.
Once the concept has been established, the next stage is the design and prototyping phase. This stage involves creating a detailed blueprint of the product's specifications and creating prototypes that can be tested and refined. The design and prototyping stage is critical in ensuring that the final product meets customer needs and expectations and can be manufactured efficiently.
The testing and validation stage is next, where the product is rigorously tested to ensure that it meets safety, quality, and performance standards. This stage involves a range of testing methods, including functional, performance, and environmental testing. The results of these tests are used to refine the design and ensure that the final product meets all the necessary regulatory and quality standards.
Once the product has been tested and validated, the manufacturing and production stage begins. This stage involves setting up the production process and creating the final product in large quantities. It also involves managing the supply chain and logistics to ensure that the product is delivered to customers on time and at the desired quality level.
Finally, the product engineering life cycle ends with the maintenance and support stage, where the product is monitored, maintained, and serviced throughout its lifecycle. This stage involves addressing any issues or problems that arise and providing customer support to ensure that the product continues to meet customer needs and expectations.
Micro-stages of Product Engineering Life Cycle
The micro-stages of the Product Engineering Lifecycle (PELC) may vary depending on the organization and the product being developed, but generally include the following:
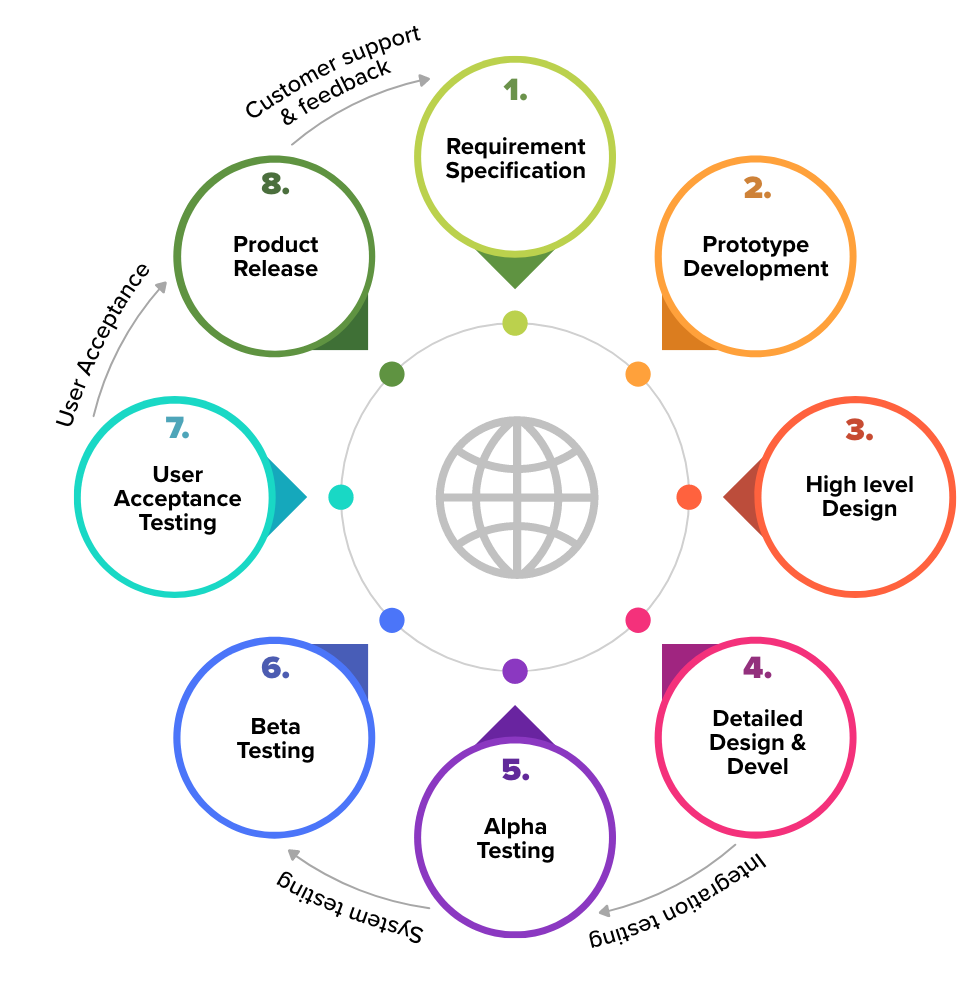
- Ideation and Conceptualization: This is the initial stage where the product idea is generated, and the requirements are defined. The product's target market, competition, and potential revenue are analyzed, and a feasibility study is conducted.
- Design and Architecture: In this stage, the product design is created, and the product architecture is defined. The design includes various aspects such as mechanical, electrical, and software components. The design is reviewed, and a prototype is created.
- Development and Testing: The product development stage involves building the product based on the design and architecture created in the previous stage. This includes coding, assembly, and testing of the product. The product is then subjected to various tests, including functional testing, usability testing, and performance testing.
- Manufacturing: In this stage, the product is prepared for mass production. The manufacturing process includes setting up the production line, creating the necessary tooling and fixtures, and conducting production trials. The quality control processes are defined and put in place.
- Launch and Support: Once the product is manufactured, it is launched in the market. The launch includes marketing the product, creating product documentation, and training the support team. After the launch, the product is monitored, and customer feedback is collected for future improvements.
- Retirement and Disposal: The product's end-of-life phase involves retiring the product from the market and disposing of it. This includes decommissioning the product, disposing of hazardous materials, and recycling any reusable components.
Factors Affecting the Product Engineering Lifecycle
The product engineering life cycle is influenced by several factors, including the complexity of the product, industry regulations, customer needs and feedback, and emerging technologies.
- Product complexity - A major factor that can impact the length and complexity of the product engineering life cycle. Complex products with multiple components and features require more design, testing, and manufacturing processes, which can extend the overall development time and increase the costs associated with the product.
A complex product, such as a new type of medical device, will have a longer and more complex product engineering life cycle than a simpler product, such as a new type of toy. This is because complex products require more design, testing, and manufacturing steps, which can extend the overall development time and increase the costs associated with the product.
- Industry regulations - They can also play a significant role in shaping the product engineering life cycle. Products that are subject to regulatory requirements, such as medical devices or automotive components, must undergo extensive testing and validation to ensure compliance with industry standards and government regulations.
Products that are subject to regulatory requirements, such as medical devices or automotive components, will have a longer and more complex product engineering life cycle than products that are not subject to regulatory requirements. This is because products that are subject to regulatory requirements must undergo extensive testing and validation to ensure compliance with industry standards and government regulations.
- Customer needs and feedback - They can also impact the product engineering life cycle. Customer feedback is essential for refining and improving the product design and ensuring that the final product meets their needs and expectations. Incorporating customer feedback into the design and testing process can help to minimize the risk of product failure and increase customer satisfaction.
Customer needs and feedback can also impact the product engineering life cycle. For example, if a company is developing a new type of smartphone, it will need to collect feedback from potential customers to ensure that the product meets their needs and expectations. This feedback can be collected through surveys, focus groups, or user testing. By incorporating customer feedback into the design and testing process, companies can minimize the risk of product failure and increase customer satisfaction.
- Emerging technologies - Emerging technologies can also influence the product engineering life cycle by introducing new design and manufacturing techniques. Keeping up with emerging technologies can be challenging, but it can also provide a competitive advantage by allowing companies to create innovative products that are faster, cheaper, and more reliable than their competitors.
Emerging technologies can also influence the product engineering life cycle by introducing new design and manufacturing techniques. For example, the development of 3D printing has made it possible to create complex products with less time and cost than traditional manufacturing methods. By keeping up with emerging technologies, companies can create innovative products that are faster, cheaper, and more reliable than their competitors.
By considering these factors and taking a proactive approach to product engineering, businesses and individuals can optimize the product engineering life cycle and create products that meet customer needs, comply with industry standards, and deliver value to the market.
Best Practices for Successful Product Engineering Lifecycle
Successful product engineering requires a combination of technical expertise, project management skills, and effective communication throughout the product development lifecycle. Here are some best practices that can help ensure a successful product engineering lifecycle:
● Define project goals and objectives: The product development team should have a clear understanding of what they are trying to achieve and what the customer needs and expectations are. This includes developing a project plan, establishing timelines, and identifying key milestones.
● Foster a collaborative team environment: Successful product engineering requires a team effort, with input from different disciplines, including engineering, marketing, and sales. Encouraging collaboration and communication among team members can help to optimize the product design and ensure that the final product meets customer needs and expectations.
● Use agile development methodologies: Agile development is a process that emphasizes flexibility and adaptability throughout the product engineering lifecycle. It involves breaking down the development process into smaller, more manageable tasks, with regular reviews and adjustments based on feedback from customers and stakeholders.
● Test and validate at every stage: Testing and validation should be an integral part of the product engineering lifecycle. This includes functional, performance, and environmental testing to refine the design and ensure that the final product meets all necessary regulatory and quality standards.
● Prioritize ongoing maintenance and support: Establishing a system to monitor the product's performance and provide ongoing support is essential to maintaining customer satisfaction and optimizing the product's performance and reliability. This includes developing a comprehensive user manual, providing product training to users and technical staff, and establishing a system for handling customer inquiries and complaints.
By following these best practices, businesses and individuals can optimize the product engineering lifecycle and create products that meet customer needs, comply with industry standards, and deliver value to the market.
Benefits of PELC
PELC ensures that the product is developed in a structured manner, and all the necessary steps are taken to create a quality product that meets the customer's needs. Here are some benefits of PELC:
- Improved product quality: PELC emphasizes a comprehensive approach to product development that includes quality assurance at every stage of the process. This results in higher quality products that meet customer expectations and have a longer lifespan.
- Reduced time to market: PELC is designed to streamline the product development process, reducing the time it takes to bring a product to market. This can give companies a competitive edge by enabling them to get their products to market faster than their competitors.
- Cost savings: PELC can help to identify potential issues early in the product development process, which can save companies money by avoiding costly redesigns and rework. By improving product quality, PELC can also reduce the costs associated with warranty claims and product recalls.
- Enhanced collaboration: PELC involves cross-functional teams working together to develop and bring products to market. This encourages collaboration and knowledge sharing across different departments, leading to better products and more efficient processes.
- Increased customer satisfaction: By focusing on the entire product life cycle, PELC ensures that products are designed with the customer in mind. This can lead to products that better meet customer needs and are more user-friendly, resulting in higher levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the product engineering lifecycle is a comprehensive process that involves several stages, from conceptualization to maintenance and support. Successful product engineering requires a combination of technical expertise, project management skills, and effective communication throughout the product development lifecycle.
By following best practices such as clearly defining project goals, fostering collaboration, using agile development methodologies, testing, and validating at every stage, and prioritizing ongoing maintenance and support, businesses and individuals can optimize the product engineering lifecycle and create products that meet customer needs, comply with industry standards, and deliver value to the market.
It is essential to adapt to changing customer needs and industry trends, and continuous improvement is crucial for success in the competitive market. reach us today at [email protected] to get assistance from our experts on Product Engineering Life Cycle.
Subscribe
Related Blogs
Trek n Tech Annual Retreat 2025: A 7-Day Workcation of OSL

OSL family came together for the Trek n Tech Annual Retreat 2025, a 7-day workcation set amidst the serene beauty of…
Exploring Drupal's Single Directory Components: A Game-Changer for Developers

Web development thrives on efficiency and organisation, and Drupal, our favourite CMS, is here to amp that up with its…
7 Quick Steps to Create API Documentation Using Postman
If you work with API , you are likely already familiar with Postman, the beloved REST Client trusted by countless…




