The use of internet has to be considered as the most powerful resource known to mankind. We have been granted with the access to information that may be tough to digest in a lifetime, thus taking full advantage of that data would be concluded as part of our own rights.
UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities recognized that the access to information should be equal for every individual. Thereby, delivering us with the powers of web accessibility.

The impact of web radically changed after the introduction of web accessibility. It not only provided everyone a chance to perceive information but also opened the doors to web and internet for everyone regardless of their physical abilities. It not only provided everyone a chance to perceive information regardless of their physical abilities but also opened the doors to web and internet. Thus, this made the developers rely on the assistive technologies for recognizing and interpreting the information.
A great deal of share can be given to assistive technologies like screen readers. In this article, we will explore how do screenreader work and how important are they.
What is a Screen Reader and How Does it Work?
Keeping the differently abled in mind, screen reader software application was introduced in the year 1939 in New York. It served people with visual impairments to use their mobile and desktop devices with its voice navigation.
There are two different ways in which this hardware lets the people provide the feedback.
- Speech
- Braille
Since the majority of the assistive technology users don’t use a mouse the application uses a Text-To-Speech (TTS) engine to translate the on-screen information into a speech. It should be noted that all the screen readers use a wide variety of keyboard commands to carry out different tasks.

A visually impaired user will use a combination of screen reader and operating system commands to achieve the tasks a system is capable of performing.
How Does a Screen Reader Interact with Browsers?
Since the larger goal here is to make the web more accessible it is impossible without the process of rendering the support of different web browser like Safari, Firefox, Google Chrome etc. Each browser interacts with a screen reader at a maximum level.
According to the Webaim screen reader user survey Safari holds the top position for both - IOS and OSx operating system followed by Firefox and Google Chrome respectively.
Safari has been a primary browser for all the Apple operating systems. Voice over is another screen reader which comes built in all the iOS and OSx devices. The operating system and the inbuilt screen reader are tightly coupled together, making it a very impressive screen reader among the people.

Further, the survey emphasized the importance of JAWS (Job Access With Speech) working well with Internet explorer. JAWS came into the market few years after Windows Operating Screen was released. Internet Explorer is a very popular and contemporary browser, and the web support of JAWS is highly dependent on internet explorer, but if the user wishes to test the traditional desktop environment on a Window platform then it has to be NVDA (NonVisual Desktop Access). Although the user can access the content on all the browsers like - Chrome, Internet Explorer, Firefox via NVDA it works best with Mozilla. The browser focuses heavily on standards compliance with the legacy of effective support.
NVDA with Chrome is a perfect combination to see if any ARIA or HTML5 attribute is not being supported by the browser or the screen reader.
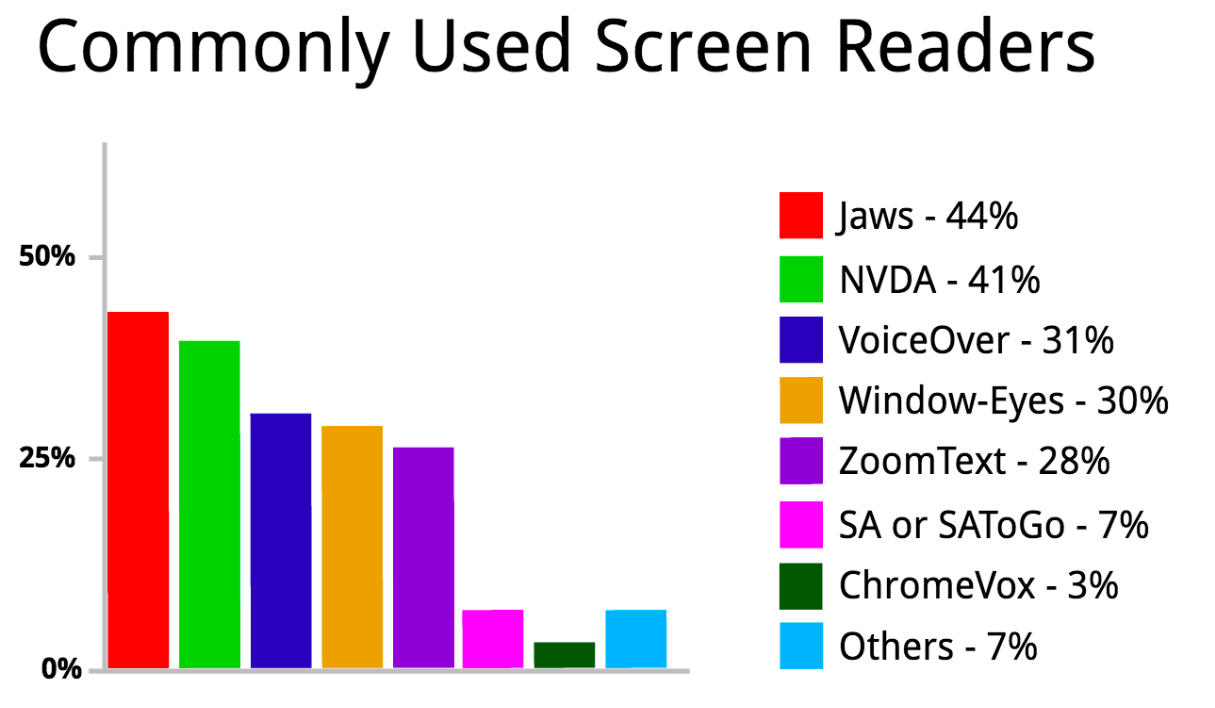
But what about the Android Operating System? The entire population access web in different modes of devices. Android handset is one of them. Talkback screen reader is specially designed for all the Android operating system. Over the time Talkback has gained a lot of support mechanism on mobile chrome. It is routinely updated with unique features and improvements. Here are some of the most popular browsers with the screen reader combinations that the audience uses.
|
Screen Readers and Browsers |
Respondents in Numbers |
Respondents in Percentage |
|
Jaws with Internet Explorer |
424 |
24.7% |
|
NVDA with Firefox |
405 |
23.6% |
|
JAWS with Firefox |
260 |
15.1% |
|
VoiceOver with Safari |
172 |
10.0% |
|
JAWS with Chrome |
112 |
6.5% |
|
NVDA WITH Chrome |
102 |
5.9% |
|
NVDA with IE |
40 |
2.3% |
|
VoiceOver with Chrome |
24 |
1.4% |
|
Other combinations |
180 |
10.5% |
Important Tools for a Screen Reader-friendly Content
There can be instances where handling the accessibility becomes difficult and might require certain tests to comprehend the task.
- HTML
Semantic HTML is accessible right after the box. It introduces the meaning to the web page rather than just presentation. Normally this type of content is only viewable by the sighted viewers, but with the help of screen reader and other assistive technologies, it is accessible to all.
- Semantic Structure
The most crucial win in a semantic HTML is to utilize the structure of the headings and the paragraphs in the content. This is done so that the screen reader users tend to utilize the headings of the document as a signpost and identify the content.
If the content has no headings, there would be huge text with no signposts to find anything. Most importantly the content should consist of logical source order.
- Native Keyboard Accessibility
There are certain HTML features that help work with the keyboard. Those elements that possess this capability are the common ones that let the user interact with the web pages. There are many users with motor disabilities that completely rely on a keyboard. In addition to traditional keyboards, many users use modified keyboards or some other hardware that replaces the functionality of a keyboard.
- Text Alternatives
This would be considered a very important tool when it comes to accessibility. The image should have a meaningful illustration description that conveys the exact meaning of the image.
It plays a vital role for the people who are visually impaired and rely on alt text for description. The text alternatives are also used for audio or to support older browsers, in such situations a simple text transcript presented somewhere on the page or on a separate page is a good idea for the diverse audience.

- Establishing the relationship with the elements
There are certain features and practices which are designed to provide context and relationship between many elements. Examples like links, tables, and data tables are included in this section.
The reason why this tool was constructed is that people using screen readers often use a common feature whereby they pull up a link to the list. The link text has to make sense out of the context.
- CSS
CSS or cascading style sheets tend to present a lot less fundamental accessibility features as compared to HTML, but it also does as much damage to accessibility if it is not used correctly. Some of the accessibility tips involving CSS might involve:
Using up of the correct semantic elements to mark up a different type of content in HTML. If the user is interested in creating a different visual effect, then CSS is the best option for them.
Verify that the source order is correct and makes sense without CSS. CSS can always be utilized to style the page. The user should make sure that the interactive elements which include buttons and links have an appropriate active states set, to give the user visual clues as to their function.
The following elements should also be taken into account:
- Color contrast checker
When selecting a color combination for the website, it is important to keep in mind that the background color should contrast well with the text color. This should be done to let the user understand the content as easily as possible.
- Hiding content
Since assistive technologies like screen readers read out the entire page and associate the qualities of the content based on their HTML tag, not all the content is created for screen readers.
Screen readers want that the content should be relevant with a complete sense of the source code. A crisp positioning is generally the best mechanism of hiding the content for visual effects. In other words, these styles would hide the text from all users. The text is then withdrawn from the visual flow of the entire page and it is ignored by the screen readers.
- Javascript
JavaScript consists of the same kinds of issues as CSS with respect to accessibility. Under or over the use of Javascript can be disastrous. It should be noted that the user should always use appropriate semantic HTML to implement functionality whenever it is available.
Functionalities may include:
Simple and complex functionality
JavaScript is used to enhance the functionality providing the client side with the form of validation. This alerts the user to function with the form entries quickly, without waiting for the server to check the data.
Complex functionality, on the other hand,d involves complicated form controls and dynamic contents. The non-native complicated form of controls is much more complicated because they need to involve a lot of nested divisions. The browser has no idea on what to do with them. If the user is inventing them by themselves, then they need to verify that the keyboard is accessible. The user can use a third-party framework, after carefully reviewing the options that are available to see how the accessibility is before diving in.
- WAI-ARIA ( Accessible Rich Internet Application)
If the developer has included complex widgets in the page then using the WAI-ARIA attribute like “roles” and many others can be a plus point for the user as well. It provides the user with proper semantics for items such as updating panels or complex form controls. There are many attributes which are involved in this tool. Attributes like:
- Roles: These are the attributes which are defined on what an element is or does. Most of which are the so-called landmark roles, which hugely duplicates the semantic value.
- Properties: These are the ones which define the properties of the element. They are used to give extra meaning or semantics.
- States: These are the special properties that define the current conditions of elements, it conveys to the screen reader that a form input is disabled. The process of the States differs from the properties. Properties don't change throughout the lifecycle of any app, whereas the states can modify, generally programmatically

Best Practices for Developers Building Screen Reader Compliant Websites
The role of the creator is to make things easy for the spectators. Hence, developers are responsible for making their website accessible to everyone. The main roles of developers can be:
- Developers should construct a site with clean and accurate code. Clean and accurate codes would help technologies and browser API to communicate successfully with each other. Developers are often induced to complete the work when the application operates as it is expected. But here writing codes for computer consumption is not the purpose. Here the clean code is all about recognizing that the audience is not just a system, it is other people as well.
- Developers should use a semantic HTML that utilizes the appropriate ARIA attributes and the roles when needed as mentioned above.
- Skip Links is a feature that enables the users to easily navigate a page. Imagine having to tab through the entire header and menu on every page just to get to the content- that could be a task, right? Hence skip links are one such feature which is provided by the developer to the user.
Drupal Accessibility Modules
Drupal understands the rights for everyone and believes that the web should be accessible to each audience. Hence, here are some of the Drupal modules which can help the website in terms of accessibility.
- Automatic Alternative Text: This module uses to generate an alternative information of the image.
- Block ARIA Landmark Roles: This module is adapted by block class. It adds additional elements to the configuration form that allows the user to assign ARAI landmarks.
- CKEditor Abbreviation: This adds the button to the CKEditor for inserting and editing abbreviations.
- CKEditor Accessibility Checker: This module enables the checker plugin. It lets the user inspect the accessibility level for the content creator.
- High contrast (beta): It allows the user to switch between active themes and high contrast versions.
Read more on how Drupal is ensuring the web accessibility standards.
But Why adopt Web Accessibility?
After reading all about web accessibility, it is natural to come across a question like - why it should be adopted and that why it is important?
- Legal/ ADA compliance
After the group or a user made claims that their website failed to provide accessibility to all the users, a legal scrutiny was brought under. These cases are prosecuted under the Americans with Disability Act and this is what makes the whole situation complicated. ADA compliance for websites states that all electronic and information technology must be accessible to people with disabilities. The ADA Standards are established to design the requirements for the construction and the alteration of the facilities that are subjected to the law.
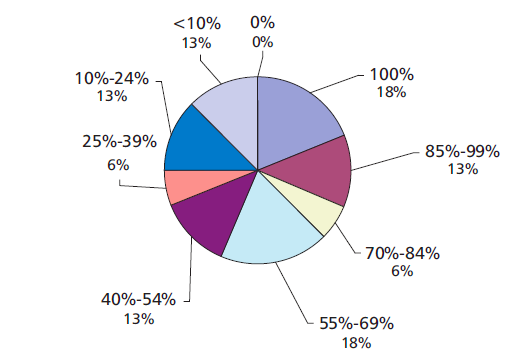
According to the U.S. Census data, about the 19 percent of the population (approx 56.7 million or one in every five people) has a disability. In other words, about 8 million people have a low vision which eliminated a square amount of audience. Thus without the use of accessibility functions, the environment for people with disabilities would be suffered.
- User Experience
As the rights stated all the user should visit the website without the legal reason. Too often, the web professionals place the users and the technology in an archive. Where UX professionals view accessibility from a human and user perspective, the technical search engine optimization (SEO) professionals view the accessibility purely from a technology perspective.
Thus, website accessibility leads to a scenario of creating an online environment in which all the users, and not only those with the disabilities, are permitted to navigate and interact with a certain understanding of the website content.
Conclusion
Adapting to the best accessibility practices is like opening up to more opportunities for your website.
Web accessibility should always be at the back of each developers mind. That ensures that the organization is open to all. At OpenSense Labs, we ensure that no stone is unturned and hence provide the best accessibility practices. Drop a mail on [email protected] to make your website comply with WCAG rules.
Subscribe
Related Blogs
Trek n Tech Annual Retreat 2025: A 7-Day Workcation of OSL

OSL family came together for the Trek n Tech Annual Retreat 2025, a 7-day workcation set amidst the serene beauty of…
Exploring Drupal's Single Directory Components: A Game-Changer for Developers

Web development thrives on efficiency and organisation, and Drupal, our favourite CMS, is here to amp that up with its…
7 Quick Steps to Create API Documentation Using Postman
If you work with API , you are likely already familiar with Postman, the beloved REST Client trusted by countless…




