You may have left for an outstation trip leaving the house door open. Or your city's waste management department may need to know if the trash cans in a locality are full to the brim. Also, carbon dioxide emissions from factories may have to be monitored remotely. All such situations call for Internet of things that gives you the power of connectivity to control and monitor seamlessly. Integration of IoT with Drupal’s robust content management framework can be highly effectual in facilitating the business workflow of your organisation.
It’s great to witness the changes from the pre-internet era to this world of connected people through all sorts of technological advances. Websites are an ultimate medium of offering a great digital business experiences to the users. Drupal is one notch higher than the rest and its flexibility has made it possible to incorporate benefits of a futuristic technology like IoT into your websites.
Evolution of Internet of Things
It is interesting to see such an innovative piece of technology steadily taking centre stage. But how did something like IoT came into being? Postscapes compiled a fascinating timeline. First ever IOT device burst into the scene when a toaster was created for the INTEROP Conference in 1989 that could be controlled over the internet. 1991 saw the first ever website going live.
In 1993, a Trojan Room Coffee Pot, created by University of Cambridge, could monitor the pot levels and send the data to the server. It wasn’t until 1993 when the term ‘Internet of Things’ was first coined.
A discernible evidence of the growth of IoT, which was being seen as a force to reckon with, was seen during 2006 to 2008 when the European Union realised the potential that IoT had to offer to the world. A European IoT conference was held to discuss the enormous possibilities of enabling IoT.
Thus, around 2008-2009, IoT took a new avatar as this was seen as the birth of a new era with more things connected to the internet than the people as was stated in a report by Cisco. In 2011, Internet of Things made it to the list of Gartner Hype Cycle for the emerging technologies.
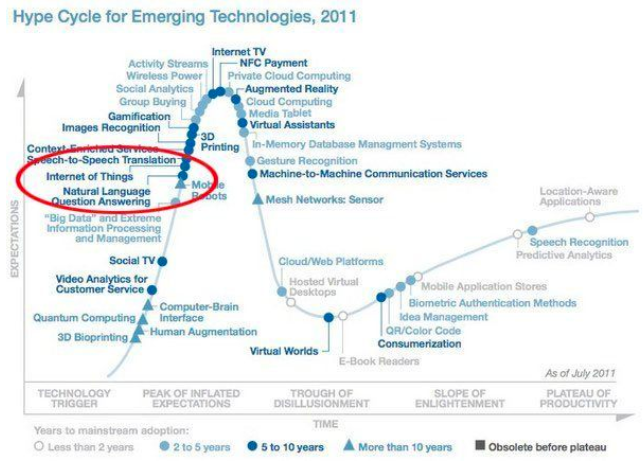
In 2017, Gartner mentioned IoT platform in its list of Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies. We will see how Drupal can be efficacious in building an IoT platform later in the blog.
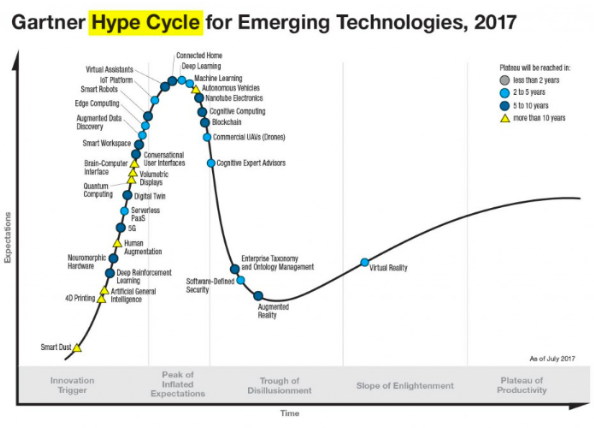
Although both the IoT and the website saw the emergence almost at the same time, websites have seen a massive growth. Drupal can lay the perfect foundation for an IoT platform.
The Architecture of the Internet of Things
Gartner defines IoT as the network of physical objects that contain embedded technology to communicate and sense or interact with their internal states or the external environment.
Prime characteristics of the Internet of Things can be described as below:
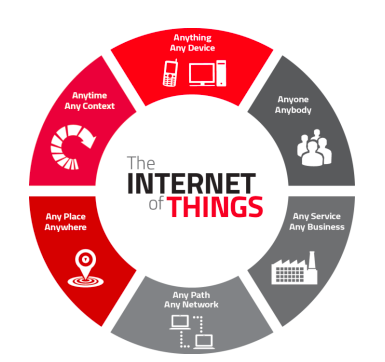
- Network accessibility, compatibility, and interconnectivity: Amazing connectivity features of IoT help in providing network accessibility which basically means getting on a network. It also lends compatibility which gives the common ability to consume and produce data. Moreover, it provides interconnectivity that permits anything to be catenated with the global information and communication architecture.
- Adhering to the constraints of things: It can provide things-related services by adhering to the constraints of things. For instance, privacy protection and semantic consistency between physical objects and their associated virtual things.
- Heterogeneous devices: IoT devices are characterised by their heterogeneity. They can interact with other devices and service platforms through different networks.
- Scalability: Devices that need to be governed and that communicate with each other will be greater than the ones connected to the internet. Handling the data generated and their interpretation for application purposes is even more pivotal in such cases.
- State of devices: It is characterised by dynamic changes in the state of devices. For instance, it can either be connected or disconnected depending upon the conditions. Furthermore, the context of devices like location and speed can very different too.
- Security: Safety of both the personal data and the physical things are of paramount importance. Security paradigm that scales with the deployment of endpoints, networks and the data that moves across all of it needs to be taken care of.
IoT architecture comprises of 4 key layers of technologies that form the pillar of support for the IoT.
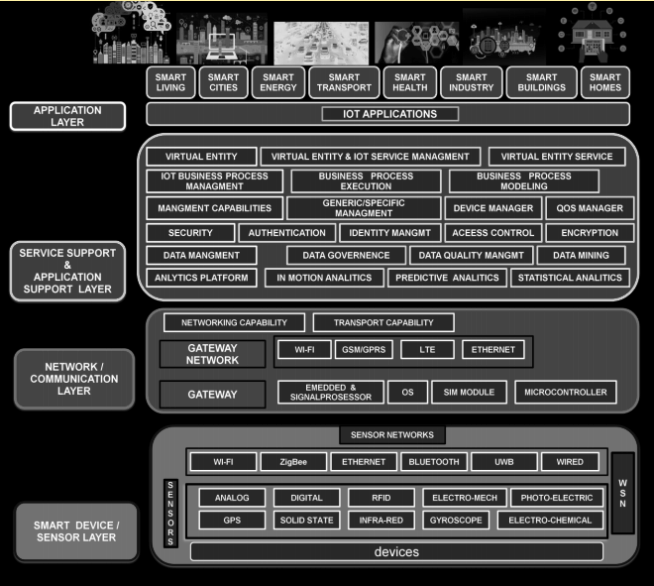
- The lowermost layer consists of smart objects incorporated with sensors. They provide the IoT devices with the characteristic feature of interconnectivity by allowing real-time data collection and processing between the physical and digital worlds. For instance, they can come in handy in measuring and recording temperature, pressure, air quality, humidity etc.
- The second layer comprises gateways (microcontrollers, microprocessors etc.) and networks ( WiFi, GSM etc.). An enormous amount of data produced by sensors needs a transport medium in the form of high performing gateways and networks.
- The third layer forms the management service layer which has the functionalities like the management of devices, analytics platform, process modeling and secure handling.
- Finally, the uppermost layer signifies the application layer which is the amalgamation of the first, second and third layers put into practical use.
Applications of the Internet of things

Internet of smart environment
Keeping your environment safe and future-secure has been streamlined by IoT. Be it air pollution monitoring, forest fire detection, weather monitoring, checking water quality, controlling river floods, and protecting wildlife, IoT can be applied to a great effect. For instance, Bigbelly’s solar-powered trash can alert sanitation crews when it is full.
Internet of smart agriculture
Farmers and agriculture engineers can leverage the benefits of IoT for efficient farming. IoT smart devices allow you to monitor greenhouse gases to maximize the yield, control humidity and temperature levels in the compost, locate and identify animals grazing in the open pastures, monitor offsprings in the animal farms, etc. For instance, WaterBee is a smart irrigation system which helps in collecting information on soil content to help reduce water wastage.
Internet of smart energy

Controlling the flow of energy from wind turbines, controlling AC-DC power supplies, and optimising the performance of solar energy plants are some of the advantages of using IoT in the smart energy consumption. GE wind turbines use sensor and grid data to reduce costs of producing clean energy and increase electricity production.
Internet of smart cities
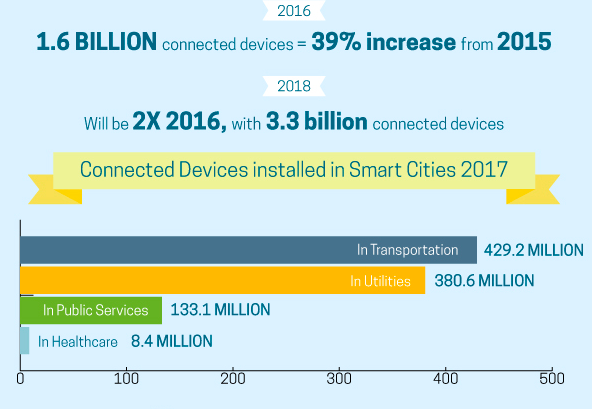
It can be used in the cities for monitoring material conditions in buildings, smart fire management systems, weather-adaptive lighting in the streets, intelligently sending a warning to take diversions in case of any unexpected event on highways, and real-time monitoring of parking space availability. OnStar’s automatic crash response uses sensors to detect vehicle crash and send alerts to the concerned authorities.
Internet of smart health
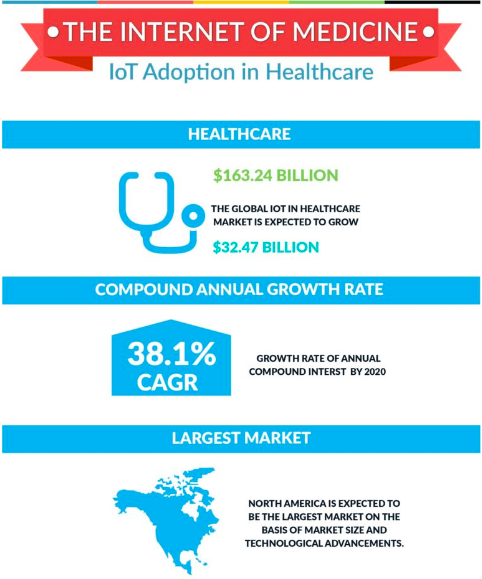
IoT smart devices can be highly useful in smart surveillance of patients, controlling conditions inside a freezer which store vaccines, and fall detection of independently living elderly people. Shockbox can be fit inside a helmet which uses sensors to detect any collisions.
Internet of smart lifestyle
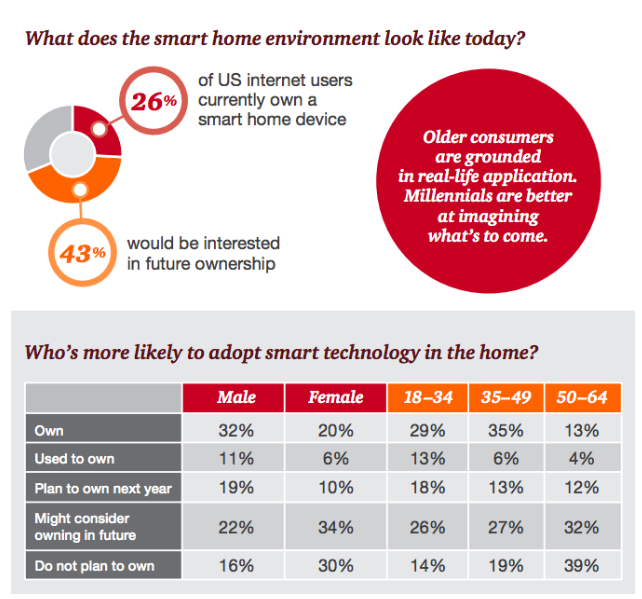
Smart living is possible with IoT as it allows the appliances to be remotely switched on and off, detects window and door openings, monitors home safety through cameras and home alarm system, and monitors water supply consumption. Belkin Echo Water uses sensors to track water usage in a household.
Business importance
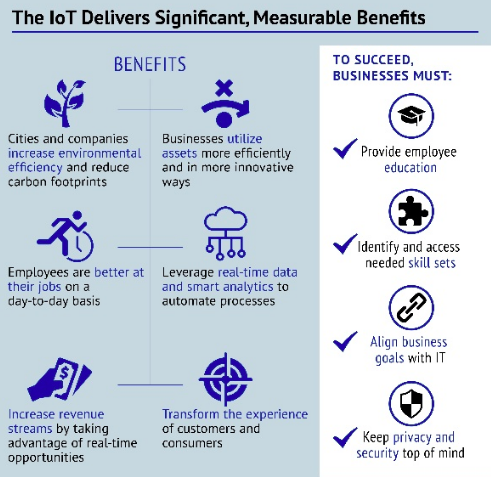
IoT can be highly effective for your business growth with a superabundance of advantages. Some of the most important benefits include:
Better customer service
Attracting new customers, reward the new loyal and regular ones, and understand the behaviour of people in and around your premises can be really useful. Connected devices help in making that a reality. For example, Amazon Dash Button helps you in ordering your favourite products with a simple click.
Efficacy in business functioning
Efficacious functioning of business is of utmost importance. Internet-connected devices have the ability to gather and assess data and share them with other devices. Sisense enabled bulb connects to the Sisense analytics platform which can be programmed to change colour to reflect performance on certain metrics. So, if the daily sales target is met, the bulb can show a green light.
Remote business functioning
Business chiefs may have to travel places to supervise the progress of a project. IoT helps them in remotely turning an equipment on and off and monitor the activity in the office irrespective of their physical location. Rolls Royce, one of the leading automobile manufacturers, has raked in a lot of money through business insights they have generated from clients through remote monitoring.
Easily track inventory
Keeping track of business workflow can be streamlined. Your business might be dealing with a plenty of raw materials, components, and finished products which can turn out to be difficult to keep a track of. The internet-connected system of sensors enables in tracking down each stage of business workflow whether it is in the factory or a warehouse. RFID chips can help track inventory movements across a supply chain and within the garments store itself.
Saves business costs
IoT can help cut business costs through proper monitoring of usage of organisational spaces. Business organisations may lead a tough time in monitoring empty conference rooms with air-conditioners turned on. Connected devices let you control and monitor usage levels. Magnet 360, which helps businesses use the Salesforce platform realised that their system needed an upgrade. Through sensors, that could analyse air flow, they could cut down energy cost by up to 70 percent.
Consistency in production quality
Connected devices can help monitor the quality of production quality for manufacturers. In 2016, the manufacturing industry has spent $178 billion in IoT. Eaton provides on-line partial discharge sensors that perpetually monitor the insulation integrity of the medium-voltage equipment. This helps in identifying low-level capacitive discharge activity prior to insulation failure thereby optimising productivity.
Drupal and Internet of Things Incorporation
Smart wearable
DrupalCon New Orleans 2016 had a session which talked about bringing Drupal and internet of things together.

It showed a demonstration that used a barometric pressure sensing, GPS-enabled wearable armband connected to the internet. It could, then, display an icon to provide the weather forecast for the current location.
The armband, which was tethered to iPhone, used mobile data to send latitudinal and longitudinal data to a ThingSpeak channel(an API for the Internet of Things). It, in turn, sent this data over HTTP to the Drupal 8 site to track the location of a ship. When the Drupal 8 website received this authenticated POST data, it created new location nodes, updated the map and table that is built with Views, and altered a block on the sidebar to show the matching icon of weather in the current location of the ship.
A presentation at DrupalCamp Oslo 2015 had a number of demonstrations to show how Drupal can be integrated with IoT technology.

Offline Status Checker
One of the first use cases was the Offline Status Checker. It was a simple demo where ESP8266, WiFi microchip with full TCP/IP stack and microcontroller capability, and a LED light was used. If the maintenance mode on Drupal 8 site was toggled to turn it on, LED light glowed red and if the maintenance mode was turned off, then the light glowed green. Basically, front page of the Drupal 8 site was queried to verify if the site is online.
Toggle maintenance mode with a TV remote
Another demo in the same presentation was called ‘Toggle maintenance mode with a TV remote’. A microcontroller received a infrared signal which was programmed to recognise on/off buttons of a TV remote. That means, it recognised only the on/off button and when it did, maintenance mode on the Drupal site was toggled.
Monitoring temperatures using Raspberry Pi
In addition to these, Raspberry Pi was used to remotely monitor temperatures and post them as nodes. Raspberry Pi, small and affordable computer used to learn programming, had a sensor attached to it to sense temperature every 3 minutes and send it to an endpoint using an API key. This API key was valid for one user and for every valid key, Drupal site allowed the posting of the node.
Arduino board integration
Arduino board, which senses the surrounding by receiving the inputs from sensors and controls lights, motors and other actuators, was integrated to a decoupled Drupal site in another demonstration. So, addition of new node of a picture of dog was recognised by Arduino board which, in turn, toggled the maintenance mode of decoupled Drupal site.
Future of Internet of Things
Predictions 2018: IoT moves from Experimentation to Business Scale, a report by Forrester, compiled some interesting facts about the internet of things and its steadfast growth.
Voice-based services would be the key part of business plans to be rolled out in the coming future.
Also after passing GDPR, the European Commission will issue guidelines to encourage the use of this technology and facilitate their the economic growth. This is because only 45 percent of data and analytics decision-makers at US organisations say they have commercialised their data while only 35 percent of those at French organisations and 38 percent of those at German enterprises do so.
Deployment of business processes that requires local data analysis close to the connected devices to enable these processes would take momentum.
Those who have been building industrial IoT platforms would exit the IaaS business.
There will be the danger of more IoT-related cyber attacks both on endpoint devices and on the cloud backplane as hackers set out to compromise systems to extract sensitive data.
Maturation of IoT and blockchain tech giants would drive blockchain adoption in the coming years.
Conclusion
Internet of things can bring the world closer. Amalgamation of Drupal and IoT can lead to something unique with Drupal’s flexibility in content management and IoT’s seamless connectivity between devices.
Reach us out at [email protected] to get the best of the internet of things and Drupal for your enterprise
Subscribe
Related Blogs
Drupal's Role as an MCP Server: A Practical Guide for Developers

"The MCP provides a universal open standard that allows AI models to access real-world data sources securely without custom…
What’s New in Drupal CMS 2.0: A Complete Overview

"Drupal CMS 2.0 marks a significant change in the construction of Drupal websites, integrating visual site building, AI…
Drupal AI Ecosystem Part 6: ECA Module & Its Integration with AI
Modern Drupal sites demand automation, consistency, and predictable workflows. With Drupal’s ECA module, these capabilities…




