Ever felt so intrigued by the movie that you were watching in a cinema hall and were completely immersed in it? Not only sometimes it can make you reminisce about instances from your own life but let you identify yourself with the characters in the film. You can start feeling like you are part of the film only to realise in the end it was just a film after all. Immersive experiences can happen in a spectacularly made film. To take the immersive experience to the next level, virtual reality is the answer.

“If they struggle with this because they are more visual learners, he asks them to put on their virtual-reality headsets for an excursion, say, to ancient Egypt.” - Washington Post
Virtual reality has seen a surge in the 2010s with 92% of the respondents surveyed in the United States in 2017 being aware of this term. Another survey in 2017 reveals that 47% of the respondents love the feeling of entering into the new world through VR. Such is the growth of VR that wide array of possibilities have opened up in different fields for its implementation. Drupal, which keeps itself relevant to futuristic technologies, offers a superb content management platform for building virtual reality solutions.
Before we delve into Drupal’s greatness in VR-based futuristic solutions, let’s decode the term ‘virtual reality’.
Defining moment
You probably must have seen some wacky headsets using VR technology. So, what is a virtual reality? Gartner, research and advisory firm, states that “VR provides a computer-generated 3D environment that surrounds a user and responds to that individual’s actions in a natural way, usually through immersive head-mounted displays and head tracking”.
It further states that in the VR-based application, “gloves providing hand tracking and haptic (touch sensitive) feedback may be used as well. Room-based systems provide a 3D experience for multiple participants; however, they are more limited in their interaction capabilities”.
Entering a whole new world without ever setting a foot there is one of the stupendous merits of VR. But how did something like this burst onto the scene?
Tracing the trodden path
Evolution of virtual reality can be traced as far back as the 1800s. Charles Wheatstone’s vision of creating a three-dimensional effect led to the invention of Stereoscope whose methods sowed seeds for modern-day products.
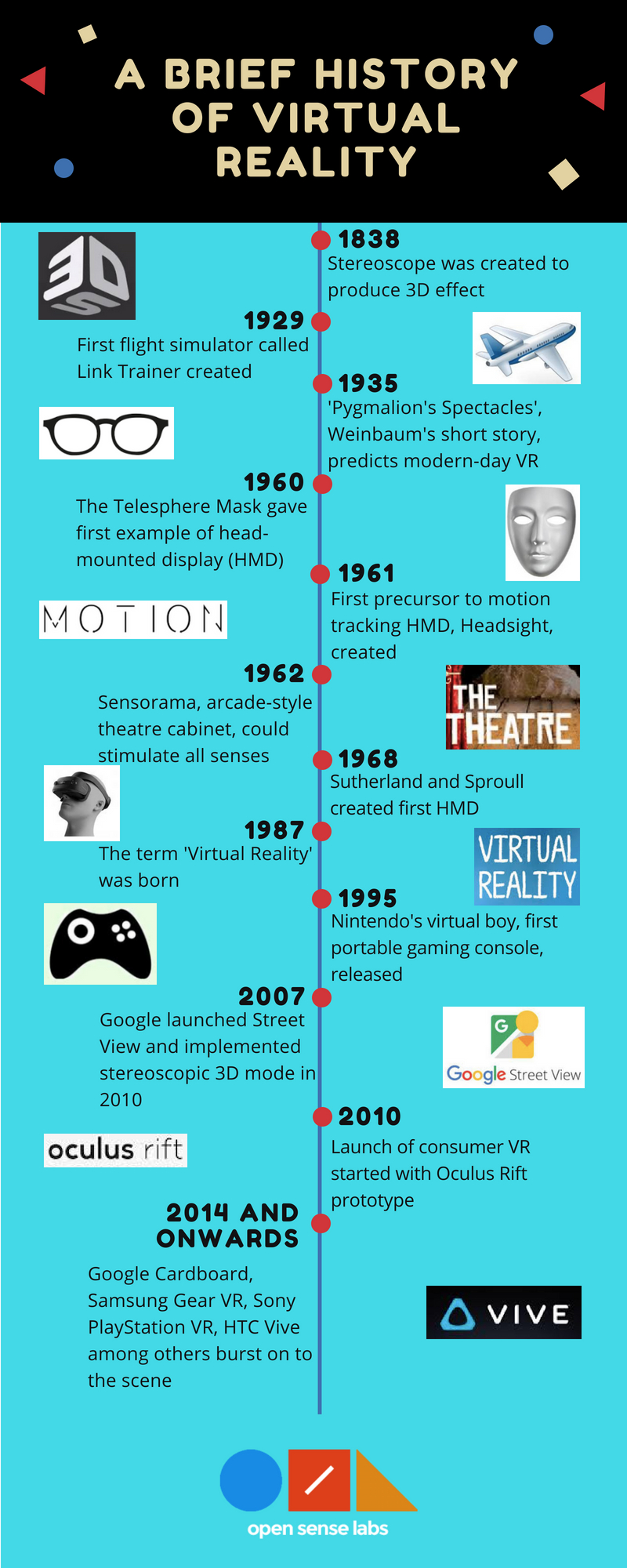
It was in the 1960s when VR devices actually started to come into the picture through head-mounted displays (HMD). Discoveries like Sensorama and The Telesphere Mask paved way for first HMD in 1968 by Ivan Sutherland and his student Bob Sproull.
Co-founder of Visual-programming Lab (VPL), Jaron Lanier, is often credited to the coinage of the term Virtual Reality in 1987 which is also believed to be popularised in the same period.
Subsequent discoveries have led to the advancement of VR technology in the 21st century. VR has seen a rise in the commercial availability through products like Oculus Rift, Samsung Gear VR, Sony’s PlayStation VR, Google Cardboard, Microsoft HoloLens and HTC Vive.
Working Principle
Immersive experiences created by virtual reality can transport you to as far as the moon to as deep as the ocean. So, how does it work? Commonly, VR relies on headsets which are also known as the stereoscopic display for building immersive experiences using two small screens for each of the eyes. These headsets are referred to as head-mounted displays (HMDs).
Accelerometers and position sensors that are found within the HMD gives required inputs for making the experience responsive. Users can also wear VR gloves that help in tracking their hands and simulate textures and objects.
Binaural microphones are used for simulating 360° sound which is used to record the way refraction of sounds happen around human head and ear. These microphones are combined with ambisonic or 3D audio that responds on the basis of where a person is looking for making the experience even more realistic.
What is the difference between augmented reality and virtual reality?
Whether it’s the term ‘reality’ that tails these two technologies or the immersive experience that they offer, VR and AR do sound similar. The perennial question that haunts many web shenanigans is vis-à-vis the difference between them.
|
Virtual Reality |
Augmented Reality |
|
Creates an interactive 3D world effect where objects have a sense of spatial presence |
Altered form of reality where content superimposes real-world surroundings |
Essentially, augmented reality, a precursor to a fully immersive VR experience, is an altered form of reality where content superimposes user’s real-world views. On the contrary, VR lets the user feel like they are in an entirely different world. So, whatever you see and experience in VR is different from what’s actually in your surrounding.
Applications of Virtual Reality
‘The Matrix’, 1999 science-fiction film, shows a VR simulator where human beings are placed within some sort of suspended animation. They are unknowingly trapped in a program called The Matrix.
Can something like that really happen? It’s debatable and let’s suffice to say that there are different possibilities that can bring a world of betterments in various sectors. Let’s look at some of them.
Healthcare
A study conducted by Duke University shows that paraplegic patients regained some control over their bodies by moving simulated limbs using VR. This was so helpful that many patients got upgraded from full paraplegics to partial paraplegics.
Tourism
Visit Wales created VR videos in 2017 to promote tourism in Wales and encourage travellers to visit the country. These videos included beautiful scenes of water bodies, dolphins, birds, and other wildlife that Wales has to offer. 85% of the people who watched these videos indicated that they would visit the location that was shown.
Marketing
Volvo’s EX90 experience helps users to go for a virtual ride in a car. This may not completely replace a test drive, but would definitely intrigue more people to visit the automobile store to see the car in person.
Journalism
From the New York Times VR films for VR journalism to the Guardian’s 6X9 project that explores solitary confinement, there is no end to the different ways it can be used.
Sports
NextVR has worked on the US Open tennis tournament and many boxing matches in addition to a live Coldplay gig.
Construction
Iris VR allows architects to take their clients on a VR tour of the building design before building them thereby enabling vital opportunities for feedback and changes.
Gaming
Yokey Pokey, A VR arcade, has 42 headsets including Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, Samsung Gear, and Playstation VR with about 30 gamers simultaneously able to play at peak times.
Drupal and Virtual reality: Use cases
There are future technologies like blockchain, augmented reality, Interplanetary File System etc. that are blowing horns in full volume letting us know that they are here to stay. Being one of the leading content management systems, Drupal leads by an example when it comes to innovating with technologies outside of its periphery. The Drupal community has been constantly engaging itself with experimentation using such technologies by leveraging Drupal’s astounding content management platform.
Well, for the starters, there is no end to the interest and the passion that web chefs in the Drupal Community show to the innovative technologies. They embrace them with open arms and that was pretty evident in the DrupalCon Los Angeles 2015.
A 360° group photo in virtual reality was organised that made it possible to walk through the Conventions Center in LA and be a part of the community virtually.
There are many use cases that delineate amazing possibilities with Drupal and virtual reality.
Virtual Postcards
DrupalCon Nashville in 2018 had a plethora of exciting stuff to talk about. One of those things was the out-of-the-box use of VR to scan guests with 3D/VR postcards. Two iPads were used to scan visitors using itSeez3D, mobile 3D scanning application, who were interested to explore VR.

In the background, the models were delivered to an endpoint that would get the OBJ file. It would, in turn, upload it to a Drupal 8 site, powered by Drupal distribution Contenta CMS, and compose it into a small virtual postcard.
VR editor
DrupalCon NashVille 2018 also unveiled a VR editor built using Drupal as the backend and React as the frontend. This VR editor can be used to merge 360° photographs, sounds, and annotations into immersive experiences. These immersive experiences could be delivered in the browser on mobile devices using a VR-capable device and on desktops with VR hardware.

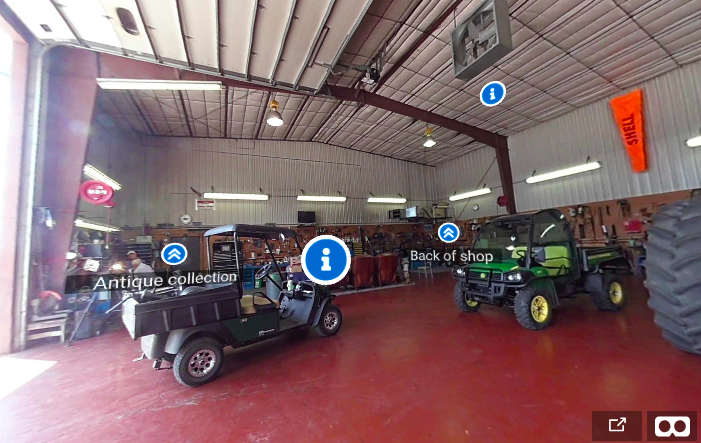
A 360° VR tour of Carrol Etchen’s shop complex near Clear Lake, Iowa, was created using EditVR. It shows a collection of cars, trucks and tractors in a farm hall with icons depicting information about the objects and takes you to the next hall through arrow icons to explore more about the shop.

WebVR
WebVR, a JavaScript API, uses VR headset like Google Daydream and a VR-capable device like Google Pixel for building immersive 3D experiences in the browser.
In a presentation given in Decoupled Developer Days in 2017, Drupal’s power in the content modelling in combination with virtual reality technologies was demonstrated. They exhibited an alpha Drupal-backed WebVR editorial studio through a model of a JSON-API compliant Drupal API. Waterwheel model and React were used to interface Drupal APIs and render dynamic experiences.
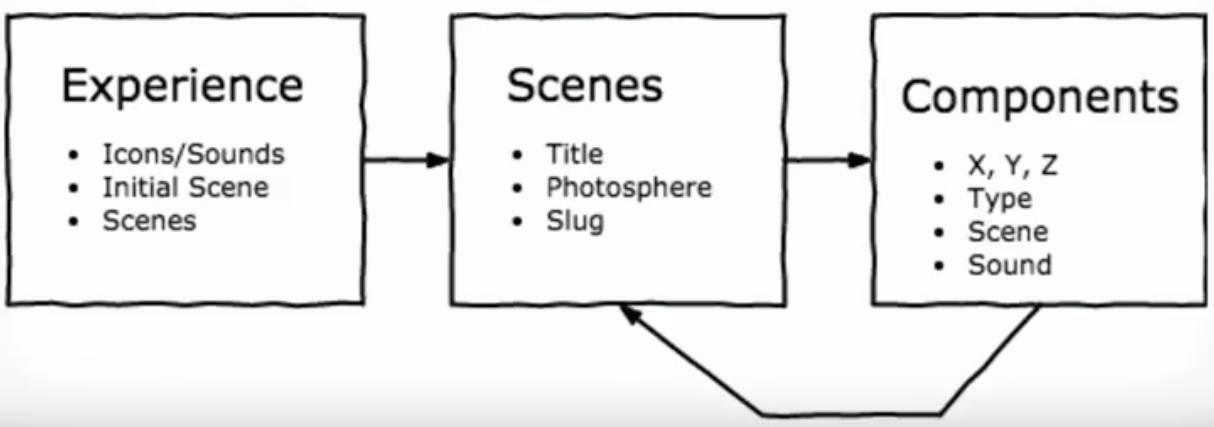
The WebVR model consisted of information icons, ambient sounds, initial scene for VR tour, references to the scenes, coordinate system (X,Y,Z) etc. In this model, Drupal was, basically, used to consume data. So, entities like information icons and scenes were pulled from Drupal, rendered, and patched back to Drupal.
Drupal’s mastery in giving content editors the freedom of creativity and its greatness in content governance was on full display.
For instance, you can roam around the 360° visuals, look at the paintings on the wall with an information icon adjacent to it telling the user what that object is. You can drag and drop an information icon and place it over a different object. Or, click on an information icon hovering over an object and change the description of the object to make it relevant. Thus, Drupal’s mastery in giving content editors the freedom of creativity and its greatness in content governance was on full display.

For optimising performance, WebVR experiences should be focussing on reducing the discomfort for the people by maintaining a consistent and high frame rate. This can, otherwise, give them motion sickness.
And in case, users do not have a VR-capable device, use Progressive Enhancement. This means you must assume that the user is using a keyboard, mouse, touchscreen and other such traditional input without any access to a VR headset. Also, you should be adaptable to changes in input and headset availability at runtime.
VR tour of University
One of the important aspects of content strategy for higher education websites is allowing the prospective students to take a digital tour of the university. Universities can use VR tour to build cross-channel experiences.
A Drupal agency developed a decoupled React VR application on top of Drupal 8. The Drupal site of Massachusetts State University (a fictional university) stored all the content and the media that will be featured in the VR tour. Media and position hotspots could be directly uploaded by the site administrators within the Drupal backend. The React frontend pulled in data from Drupal using JSON API.
For instance, if a student would want to explore more about the university, he can take a virtual tour inside the 4 walls of his room. All he has to do is place his phone in a VR headset which would then allow him to wander the university campus, see the buildings, and view images, videos, program resources within the context of the tour.
How the future of virtual reality looks like?
Peter Rubin, Author of Future Presence: How Virtual Reality Is Changing Human Connection, Intimacy, and the Limits of Ordinary Life, said in an interview to The Verge in 2018 that for VR “to become a culturally accessible mainstream consumer technology, you’re looking well past 10 years. People are working on taste and smell, though those are probably the last pieces of the puzzle that will click into place. People working on brain-computer interfaces. People that are working on anything you can imagine”.
In a Bloomberg interview, Facebook founder Mark Zuckerberg resonated with similar thoughts saying that “VR is a good candidate to be the next major computing platform.” He thinks that it will take more time to get traction but is optimistic that VR could be a primary form of communication technology in the near future.
“Virtual reality is a good candidate to be the next major computing platform”- Mark Zuckerberg
Virtual reality is going to see a rapid shift in their adoption by the enterprises. By the year 2022, the market size of virtual reality and augmented reality is forecasted to increase by mammoth levels as can be seen in the graph.
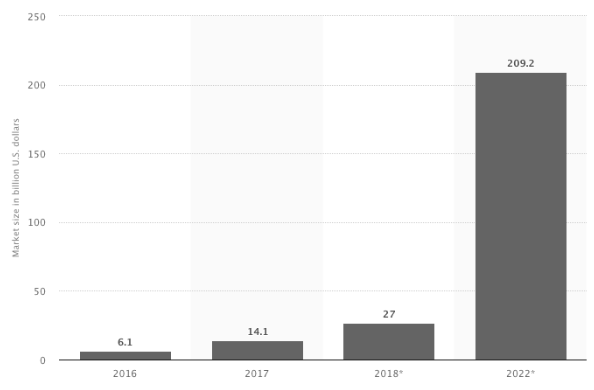
By 2025, Gaming would be miles ahead as the leader of the market revenue through VR adoption followed by healthcare and engineering.

Conclusion
Waking up from a dream may sometimes be the most upsetting thing when you realise that the world you were in just seconds ago is just a dream after all. It's everyone’s wish to escape from the reality and go into your own dream world. While you may not be able to go into the oblivion once and for all, virtual reality can let you enjoy dream world every now and then.
VR has a lot to offer with a scope for implementation in a wide variety of sectors. Using the power and flexibility of Drupal for delivering content in combination with VR frameworks, possibilities of VR applications can be thrown wide open.
After all, who couldn't use a break from reality? Engage with our Drupal experts to know how we develop Drupal-based projects. Ping us at [email protected] to build futuristic solutions like VR.
Subscribe
Related Blogs
Drupal's Role as an MCP Server: A Practical Guide for Developers

"The MCP provides a universal open standard that allows AI models to access real-world data sources securely without custom…
What’s New in Drupal CMS 2.0: A Complete Overview

"Drupal CMS 2.0 marks a significant change in the construction of Drupal websites, integrating visual site building, AI…
Drupal AI Ecosystem Part 6: ECA Module & Its Integration with AI
Modern Drupal sites demand automation, consistency, and predictable workflows. With Drupal’s ECA module, these capabilities…




