You probably would have installed a mobile app on your smartphone and wondered about its ingenious nature. One of the key reasons for the incredible performance of a mobile app is the incorporation of the right mobile application development tools right in the build stage. So, how can you choose the right mobile application development tools?

'Beyond Mobile: Surviving the Shattered Future' states that "The single screen of our past has shattered and the fragments have embedded themselves in our pockets; on our couches; and in our lives." Having the liberty to do things on the fly has been an integral feature of mobile devices which has, in turn, led to a rise in the number of mobile apps. It is important to use the right set of tools to bring out the best mobile app in the market.
Architectural constraints
There is a thin line of difference between various architecture options that are available for the development of a mobile app.
Responsive web design approach
A fully responsive website is designed with a responsive web design approach for responding to the user’s environment. This comprises of different sorts of devices, connectivity states, form factors and interaction modes. Flexible media, fluid grids and media queries are the three-pronged approaches in CSS techniques that act as the deciding factor so that the site is aptly sized and responds well on different devices.
A fully responsive website is designed with a responsive web design approach for responding to the user’s environment.
Moreover, rendering the site properly for devices with modern displays is a significant part of responsive web design approaches. Usage of expandable and compressive images, Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG), and high-DPI (Dots Per Inch) raster images are some of the advanced image strategies that are beneficial in this pursuit.
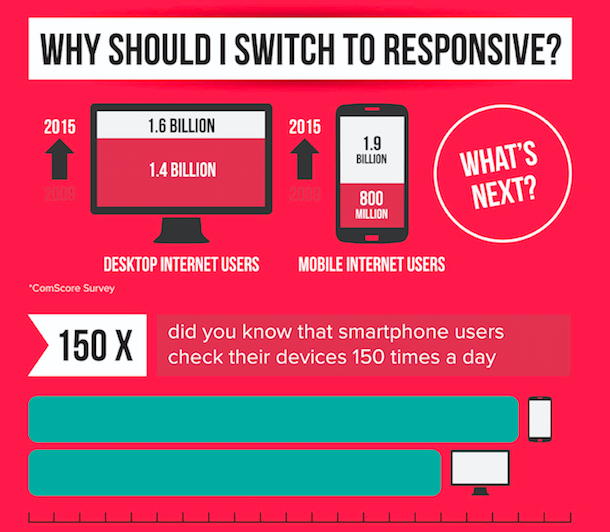
Responsive websites are cost-effective and are preferred over the development of a separate site that is optimised for mobile. It is easier to find developers who can work on responsive site development and can be developed quickly.
There are few caveats like:
- It has the snail-paced ability when it comes to adoption of the latest innovations
- It is low on performance
- It has poor integrations with more advanced features like cryptography, on-device storage, push notifications, and background sync among others.
Progressive web application
A responsive site with the incorporation of more functionalities like better offline usability, user engagement and speed is what a progressive web application (PWA) is. Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Opera are some of the examples of supported browsers that treat the website like a native application with functionalities like a home screen icon, push notifications, and offline and background access.

A responsive site with the incorporation of more functionalities like better offline usability, user engagement and speed is what a progressive web application (PWA) is.
Browsers that do not support PWA, like Safari that has minimal support, fall back to the ‘responsive website’ behaviour. But it may still reap the merits of the optimisations that are performed as part of the PWA incorporation.
Moreover, ‘native-like’ features are typically incorporated in PWA even though they are technically not part of the PWA minimum requirements. For instance, native/web credential sharing, Google Payments API, geolocation, deep linking etc.
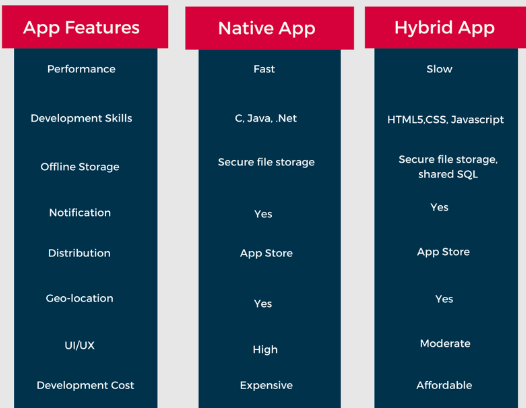
Hybrid architecture
At the heart of the hybrid architectures, one thing is common - a native application that relies on webviews in order to render and serve content. In a hybrid application, you have to decide where on the native-to-web spectrum your app is a part of as the decision isn’t binary.
In a hybrid application, you have to decide where on the native-to-web spectrum your app is a part of as the decision isn’t binary.
Taking a shell of a native app and rendering the content and UI controls in a web view is one of the approaches for building hybrid architectures. Then, native functionalities like interactive push notifications can be put in to make an application feel more native. This helps in moving swiftly when less native-required functionalities are needed and the UX is not critical.
One of the most important tools for this is Apache Cordova but with the availability of Progressive web applications, React Native/ Xamarin and fully native options.
Mostly native controls are used by a robust hybrid app for navigation and webviews are used for rendering content. Or, it can use a temporary fallback for new or seldom accessed content until a native version can be built. Such an approach can be valuable for dynamic views that must look identical across different platforms. For instance, a railway application might use a webview for rendering a boarding ticket from the same code on Android, IOS, and mobile web.
A novel approach is to leverage webviews for new content or new content types. Replace them with native experiences in accordance with the capacity of your development team. This approach is used by the hybrid architecture of Basecamp 3 by loading all of the content from a URL. The native control is shown if the app’s router finds a native control for administering the URL. Or else, it is loaded in a webview. For organising the intricacy here, turbolinks-ios library can of assistance.
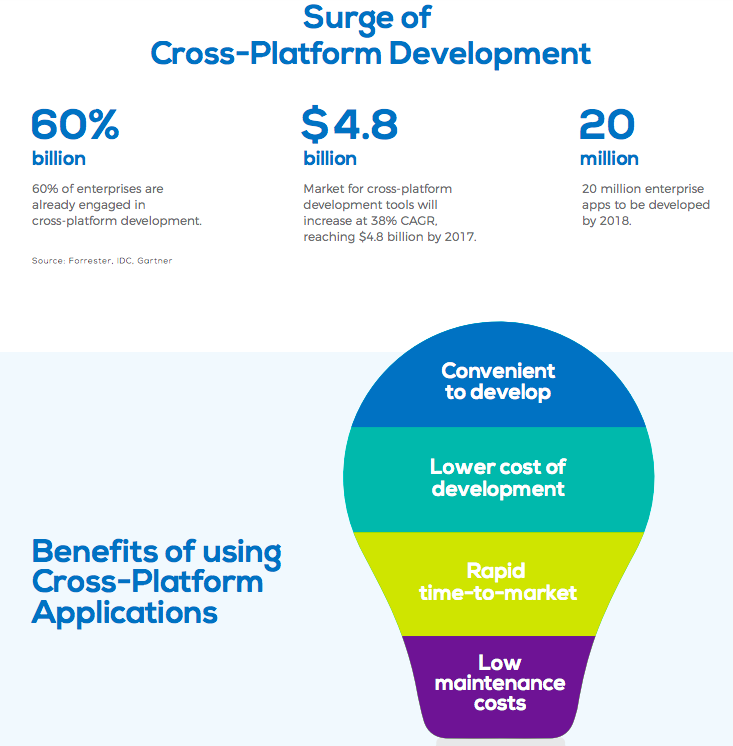
Cross-platform application
To write native mobile applications once and run them on Android, iOS, and even Windows, tools such as Xamarin (in C#) and React Native (in JS) can help. They may offer merits in letting a familiar team in speeding up but have few demerits.
For instance, these tools may lag behind the official tools thereby minimising the adoption of latest innovations. Furthermore, cross-platform tools like React Native that render UI at runtime may be sluggish. Also, some functionalities may not be available. For instance, React Native components do not run on Apple Watch.
To write native mobile applications once and run them on Android, iOS, and even Windows, tools such as Xamarin (in C#) and React Native (in JS) can help.
The cross-platform approach of React Native requires some special attention because of its usefulness. The React Native projects are written primarily in JS and are changed to native views at runtime which can be of great use - write code once that runs on both iOS and Android. Also, it is very helpful while live-updating code that makes UI iterations faster.
Some of the drawbacks of using React Native include:
- Slower application due to extra overhead of the JS runtime thread that translates your JS into native view layout code.
- Oversimplified UI of several React Native components or, a UI for either iOS and Android only.
- The application can be written completely in JS only if all the required components are available.
- The development and debugging experience for React Native projects is comparatively less friendly than Android Studio or Xcode which makes debugging time-intensive.
Fully native application
When the mobile operating system is preferred toolchain for developing applications, it is referred to as fully native application. For instance, usage of tools like Xcode and Swift on iOS and Android Studio and Java for Android.
It provides the perfect basement for the high-quality application. In this approach, graphical and app performance are faster and new innovations are built.
When the mobile operating system is preferred toolchain for developing applications, it is referred to as fully native application.
It does have few caveats like:
- The arduous task of searching for qualified developers
- App Store rules and submissions can make the release process slower
None of these limitations deters you from building a mobile-friendly site. If you have the luxury of spending time and money on an awesome experience, this might be your option for high-quality outputs.
On the path of decision-making
A thorough assessment of the mobile application development tools will help in deciding which one to use for different apps. A checklist has been laid out below to make the right decision in zeroing in on best tech stack.

Familiarity with the tech stack
If your development team knows JS, considering a web option or React Native can be helpful. In case, your team has an abundance of in-house Java experience, fully native app should be considered as the Android applications in mostly written in JS or Kotlin and the Java developers can pick up Objective-C or Swift easily. Also, if the development team is adept in deep C# and .Net, a Xamarin application with Microsoft Azure backend can be considered.
Considering fully-native toolchain
- For tablets, smart TVs or smart watches: Non-native functionalities make it difficult and even impossible to incorporate astounding non-phone features including picture-in-picture tablet video, smartwatch UI, etc. In contrast, any functionality can be implemented cross-platform using bridging. But adoption of bridging extensively should be done at one’s peril. It can make your application more convoluted, requiring more costs for maintenance. Such cutting-edge functionalities can be incorporated using fully-native solution. In case, you are going for something less than a fully-native solution, go through its support for the high-range features that you need.
- For competitive rewards: Typically, business investments are either tactical or strategic which can help decide what sort of tools you would need for your mobile application. If the mobile application is tactical, for instance, an app doled out to pay bills, less expensive option can be considered. For strategic investments, to give your enterprise a long-term benefit over the competitors, a fully native application that is individualised to the OS you are running on, can be considered.
- For best user experience: Visualise smooth animations, augmented reality, simplicity in usage for visually impaired, on-device machine learning, and more. If such things are appealing to you, fully native solution can give that ‘wow’ factor to the mobile application.
- For having Google and Apple as marketing partners: To have your app featured in Google Play or the App Store, full native solutions can help. Google and Apple can attract large number of customers to your app. So, fully native solutions should be considered for garnering large number of new downloads. In case, your app is a channel for reaching out to the existing customers, it is unlikely to get features on Google Play or App Store and equally unlikely to benefit you. There is one exception to this guideline and that is games - cross-platform games that are written using Unity are usually promoted.
- If the market is competitive: Adopting new technologies would be easier with fully native toolchain as you do not have to wait for abstraction layers or even roll your own. Innovative technologies take some time to get ported to cross-platform tools. In such a case, your competitor’s apps can outrank yours. But if the cross-platform solution provides you better team scale, for instance, if you have a great set of JS developers but limited availability of native developers, React Native can be useful which can get you moving quickly.
Considering web solution for budget issues
The web is standard and various frameworks are available to get you moving quickly. Frontend web development can be a terrific option as it is simpler and cost-effective for staffing the team.
Considering cross-platform application for identical looks
Generally, Android and iOS applications must not look and act identically. Their UI guidelines are entirely different. If you are okay ignoring most of the guidelines and building one UI for both platforms, cross-platform application can be advantageous.
Considering cross-platform or fully native application for security reasons
Cross-platform or fully native application is useful for full control of offline support, certificate pinning, data encryption and several other significant concerns and enables you to access enhanced security functionalities. Dynamic programming languages like JavaScript and Objective-C can be avoided as they are vulnerable to buffer overflow, type mutation and method swizzling than more static languages. In case, you are going for JS, for instance, React Native, consider JSX type annotations.
Considering Progressive web application for Android/Windows
If most of your users are on Android supported devices, considering PWAs can help in reaping the benefits of offline support, payments, Bluetooth integration, geolocation and push notifications among others.
Considering responsive or progressive web application if you are testing waters
For those, who are testing the market, web apps are affordable solutions and are the fastest to iterate on. In case, if you have doubts whether your product would be valuable to the end users or not, it is better to go for web app.
Considering Progressive web application or hybrid architecture for internal customers like employees
To enhance the productivity of your internal customers, better design of the app should be considered. Internal, employee-only tools, most often than not, are low on budget when it comes to design niceties. If the UI/UX is not a huge concern of your, PWA or hybrid architectures can be great.
Considering hybrid architecture for timeline constraints
Amazing native applications are of extremely top-notch quality. Similar to other high-quality goods, they do require a lot of time and developmental effort. Even the greatest developers would find native applications a huge risk if the business conditions lead to tight deadlines for a project. Considering a hybrid architecture can help in iterating rapidly with the web. Once the project deadline is surpassed, you can iteratively replace web content with the native content if required.
Conclusion
Making decisions wisely while selecting mobile application development tools is of paramount importance. Contact us at [email protected] to learn more about mobile application tools.
Subscribe
Related Blogs
Trek n Tech Annual Retreat 2025: A 7-Day Workcation of OSL

OSL family came together for the Trek n Tech Annual Retreat 2025, a 7-day workcation set amidst the serene beauty of…
Exploring Drupal's Single Directory Components: A Game-Changer for Developers

Web development thrives on efficiency and organisation, and Drupal, our favourite CMS, is here to amp that up with its…
7 Quick Steps to Create API Documentation Using Postman
If you work with API , you are likely already familiar with Postman, the beloved REST Client trusted by countless…




