Competition among companies is based on strategic partnerships. When the association is technology-based, expansion of the network happens faster, eventually broadening the industrial horizons.
The fundamental problem faced by the organizations while moving ahead with these technology-based association is the long-running obsolete business systems. These old systems are not polished enough to match the pace of current technology trends. This turns out to be the biggest barrier to the growth of an organization.

Every once in a while, a business should revamp its internal system so as to march ahead in the technology game among its competitors. The adoption of microservices and blockchain will build a strong foundation for technology-streamlined associations.
How will this happen? Let's delve in and find out how come the transformation of today will create a better future for tomorrow.
Redefining Business Systems with Blockchain and Microservices
The two technologies, microservices, and blockchain will help in the evolution of an obsolete business technology-architecture. As the applications become more modular, microservices will stimulate flexibility and enabling swift integration with new partners. Furthermore, as the partnership grows, the blockchain acts as a pivot for the creation, scaling, and management of these relationships.
A single piece of technology is not the correct term for defining microservices. It can be stated as an architectural methodology that uses a set of tools like application programming interfaces (APIs), containers, and cloud, breaking the applications into simple and individual services. It makes the application reliable and scalable and forges easy partnerships, streamlines the integration of services, with no obstruction to the partners or customers.
When it comes to blockchain, it is a distributed ledger system that stores groups of transactions (blocks) and then do the linking and sequencing of the list of transactions using cryptography. These can either be public, like Bitcoin or Ethereum or can be developed privately or by associations. Blockchain is not owned by a single organization and is distributed across a peer-to-peer network. The redundancies in the blocks and consensus mechanisms assure that the manipulation of transactions cannot be done.
The definitions stated earlier gives a rough idea about how the work happens in a microservices architecture and a blockchain system individually. But the question is what paradigm shift occurs when blockchain and microservices come together.
If microservices are fundamental to build and scale partnerships, the blockchain acts as a trigger for the management and operations in real-time. The association of blockchain and microservices will provoke businesses to maintain a higher volume of partnerships and works as a wheel between partners, without compromising the integrity and security of the products and services. Blockchain will resolve the complexity by working as a delegate for trusted relationships.
Furthermore, building trust on a blockchain ensures tracking of broader networks, onboarding new partners, and entering new ecosystems with ease. Blockchain-based smart contracts enable businesses to sketch-out relationship terms and then perform the automatic release of the data or program-execution for any prospective partner meeting those terms.
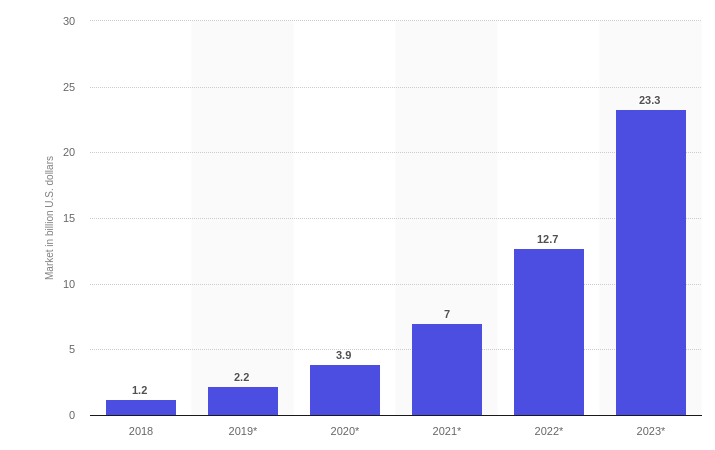
The forecast on Statista suggested, the coming years will see major growth in the worldwide blockchain technology revenues, with a rise in the market share to over 23.3 billion U.S. dollars by 2023.
Benefits Extracted from Microservices and Blockchain Association
- Because it is serverless, there is no overhead to handle servers so as to start a blockchain project.
- Smart contracts provide isolation and extensibility. Similarly, microservices provide segregation using docker container and scale the process by running multiple instances of specific microservice.
- Microservices is the best choice for designing a system that requires a sync replica of the ledger. The reason being, while doing a trivial transaction, if an operation fails, the whole system will remain unaffected.
- For the purpose of designing a microservice-based system, multiple teams can work together and test each module parallelly, eventually speeding up the rapid application development.
Drawbacks of Blockchain and Microservices Pairing
Despite the advantages, there are still a bunch of reasons supporting the fact that not every company will want to go with the blockchain microservices association.
- Blockchain focuses on the widely distributed environments whereas microservices are optimal for more centralized deployments, creating a loophole for the combination.
- Both blockchain and microservices are the byproducts of a distributed architecture, but they solve very different types of problems. For instance, blockchain is more focused on transactions enabling while microservices are focused more on streamlining speed and scalability.
Byproducts of Blockchain and Microservices Blend
#1 Fluree ‘Where Database and Blockchain Converge’
Fluree is an extensible blockchain database that imparts an enterprise database versatility to the developers by combining blockchain with microservices. It prospects a broad set of choices to streamline the system from a completely centralized static ledger to a fully decentralized network. It brings consistency, scaling, rich access capability, and many other benefits for the systems.
#2 Blockchain-Enabled Decentralized Microservices Architecture System (BlendMAS)
With the adoption of service-oriented architecture (SOA) by IoT and the cyber-physical systems (CPS), the monolithic architecture is not powerful enough to provide scalable services for a distributed IoT based smart passive sensor (SPS) system.
So as to offer secure data access control in an SPS system within an authorized blockchain network, a microservices-based security technique is put forward, termed as a BlendMAS. A journal on this was submitted to the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain (Blockchain - 2019). Here the functionality of the security services is separated into distinct containerized microservices that are built using smart contracts and are deployed on edge and fog computing nodes. This results in the formation of a decentralized, extensible, secure data sharing and access control system for a distributed IoT based SPS system.
#3 Po.et’s Module-Based Application Architecture
Po.et, a blockchain-enabled media Startup, proposed that while building a decentralized application driven by blockchain with a microservice architecture implementation in it, it required a special approach to be followed.
Initially, the traditional microservices model was adopted. But later as the project progressed, it was found out that the Po.et node is a network of decentralized nodes. Each node runs majorly like a desktop application rather than a cloud-based type. The management of nodes is done by the network itself and it does the automatic scaling with the addition or subtraction of each node. Thus the traditional microservices architecture is of no use for Po.et.
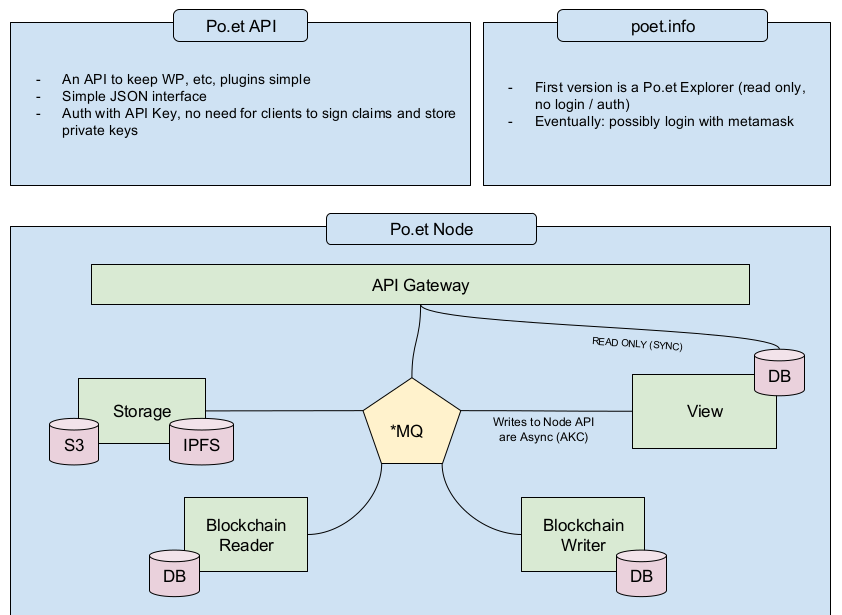
Therefore, a new module-based application architecture that is easier to set up and manage in a decentralized network, has been proposed. In Po.et’s new architecture, multiple microservices are not required for each node. The distinct modules work similarly like microservices by being in complete isolation from each other. Communication between modules happens via a message queue and enhances the efficiency and security of Po.et nodes.
#4 Ericsson Blockchain Data Integrity Microservice
Ericsson, a global ICT services and solutions provider brought together the fundamentals of blockchain, microservices, and open APIs to furnish data integrity of the blockchain, implemented as microservice for the GE Predix Cloud platform, termed as the Ericsson blockchain data integrity service.
It facilitates the generation of non-reversible signature for user data, does the verification of the available version of the signed data that remains unaltered and matches the non-reversible signature, and forges the signature extension of to the public record.
Conclusion
To stay ahead in a technology-based game, it is imperative for the companies to do the re-evaluation of their technology and the up-gradation of the system stack on a regular basis.
When blockchain and microservices are integrated, blockchain forges the secure distribution of transactional data, providing a perfect environment for the success of decentralized application solutions.
What do you think about the blockchain and microservices association? Share your views on our social media channels: Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter.
Subscribe
Related Blogs
Trek n Tech Annual Retreat 2025: A 7-Day Workcation of OSL

OSL family came together for the Trek n Tech Annual Retreat 2025, a 7-day workcation set amidst the serene beauty of…
Exploring Drupal's Single Directory Components: A Game-Changer for Developers

Web development thrives on efficiency and organisation, and Drupal, our favourite CMS, is here to amp that up with its…
7 Quick Steps to Create API Documentation Using Postman
If you work with API , you are likely already familiar with Postman, the beloved REST Client trusted by countless…