We are told from a very tender age that no-one is quite like us. We are special. But what if that is not true. There are plenty of modern-day evidence that would suggest that we all, in fact, have at least 1 doppelganger out there in this big wide cosmos. So, if the creators of the universe have the tendency to duplicate human bodies, would humans themselves leave this race?
Around 25-30% of content on the web is duplicate!
The whole point here was to fetch your attention towards the world of web pages and the significance of identical content that appears on more than one web page, in other words - Duplicate content.
Duplicate content can happen to anyone at any time.
Matt Cutts, Google’s head of search spam, says about 25-30% content on the web is duplicate. Sadly, most people don't even realize it.
Result? Hurting your own SERP since Google will penalize the duplicate content. Who would want that, right? Thus, eliminating duplicacy becomes a vital activity for the health of the website.
How do you do it? Before I dig into the solutions to eliminate duplicate content, let’s take a look at exactly “what is duplicate content?”
Duplicate Content
Duplicate content refers to the similar content that appears in multiple locations (URLs) on the web, as a result, search engines have no idea which web pages to show in the search result. When duplicate content is present, site owners suffer a huge decline in their ranking and lose traffic swiftly.
If seen from a wide spectrum it affects the search engines as well as site owners. Here is how it does it:
For Search Engines
- Duplicate content can bring hindrance to the search engines. They have no idea of the version which should be included/excluded from the indices.
- Search engines have no idea whether to direct the link metrics (authoring, trust, link equity, etc) to a single page, or to multiple pages.
They don’t understand which version to rank for the result.
For Site Owners
- The search engine would rarely show multiple versions of the same content to offer the best search experience, and thereby they are forced to select the version which is most likely to be the best result. This weakens the visibility of every webpage.
- While other sites have to choose between the duplicates as well, link equity is further diluted. Instead of multiple links pointing to one single content, they link to many pieces, spreading the link equity among the duplicates. As all the inbound links are constitutes as the ranking factor, it can impact the search visibility of the content.
Result: The content doesn’t reach the search visibility
Why Does it Happen?
Possibly one of the most recurring questions about duplicate content is why it occurs at the very first place.
There might be times when the user unintentionally didn’t copy the existing page, and yet they face it.
So, what creates it, and where did it come from?
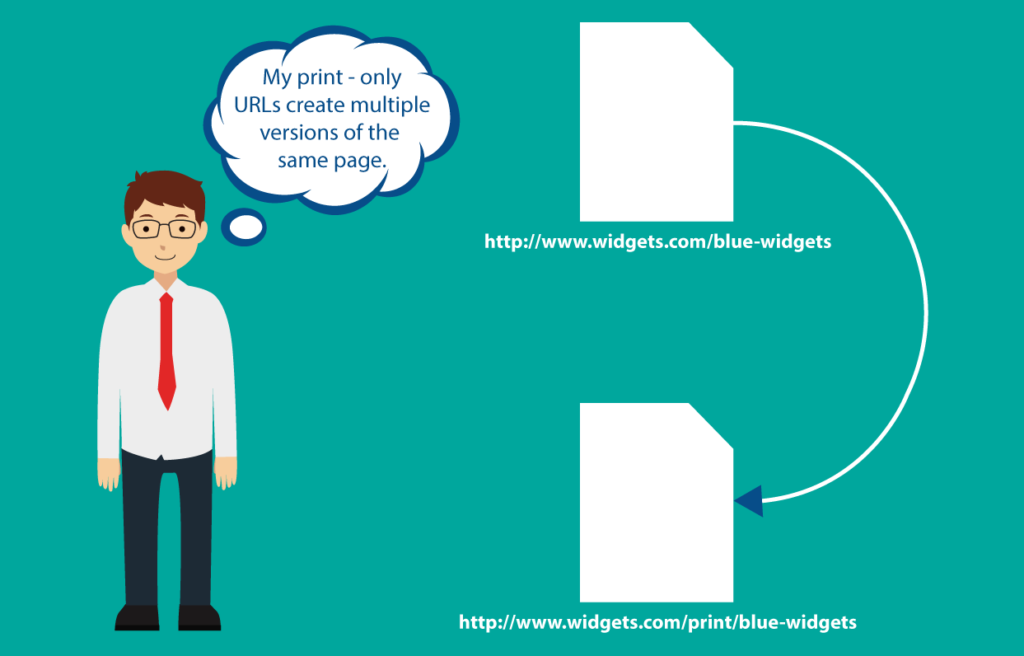
Duplicate Content takes place when multiple versions of a single page are created. This happens when the page looks identical in every contrast but the URL may be somewhat different. For example
Yet, there are numerous reasons why duplicate content knocks the door of a website holder. Let’s take a look at some more.
Types of Duplicate Content
1. Scraped content
Scraped content is termed as an unoriginal chunk of content on a particular site that has been copied or duplicated from some other website without permission. Not always does Google differentiate between the original and the copied content, it is the job of the site owner to watch out for scrapers.
2. Syndicated content
This type of content is republished in some other website with the permission of original’s piece author, meaning pushing your post (be it an article, blog post, video or any web-based content) to the third party that republishes it to their website.
You might say that this should be the legit way to bring the content in the eyes of the audience, but it should be noted when I say this - it is important to set guidelines for the publishers. The publishers in such case can opt for the canonical tag on the article to indicate the original source of the data.
3. HTTP and HTTPs pages
Oh yes, it has to be one of the most popular duplication issues. Identical URLs on the site arises when the switch from HTTP to HTTPS is not implemented with the attention of the process that is required. In other words, this scenario takes place when:
Some part of the website is HTTPs and use URLs
It is always secure to use single age or a single directory on an HTTP site. Though you should keep in mind that these pages have internal links that are pointing to the relative URLs rather than absolute URLs.
Relative URL: /use-drupal-intelligent-content-tools-module
Absolute URL: https://opensenselabs.com/blog/tech/use-drupal-intelligent-content-tools-module
It should also be noted that relative URLs does not have protocol information, instead they use a similar protocol as parent page they are located on. If the search bot locates an internal link it decides to follow it. It could continue to do the crawling by following more relative internal links, or may even crawl to the whole website, and hence index the two completely identical versions of the webpage.
The site has been switched to HTTPs, but the HTTP version is still available
This happens when there are backlinks from some other site pointing to the HTTP page, or can occur when some of the internal links on the site still carry the protocol. The non-secure pages do not redirect to the secure ones.

4. WWW and non-WWW pages
This is one of the oldest reason for duplicate contents when the site is available to both www as well as non-www. When www. is in front of a site, it appears as a hostname which can serve with versatility with DNS. This restricts the cookies when using multiple subdomains, and more. Whereas non-WWW domains also referred to as naked domains, they do not have any technical advantage.
When both versions of the site are available on the web, Google fails to recognize that which one is original, thus marking both as duplicate content.
5. Similar Content
When people specify content duplication, they often imply the scenario where there is a complete identification of identical content. Thus, the piece of very similar content falls in the definition of duplicate content for Google. There are times when a particular site copies the exact same data from another site and falls under the definition of duplicate content. Such can frequently occur with the e-commerce websites, which has similar product descriptions that only differ in fewer sections.
How Do I Fix Duplicate Content Issues with Drupal?
It is important that the CMS which you are using should know the difference between the content which suffers duplicacy and the content which is original. Drupal is one such CMS which does the task pretty well.
There are a couple of modules which helps the websites maintain the originality without compromising with the rank, and the traffic of the web pages.
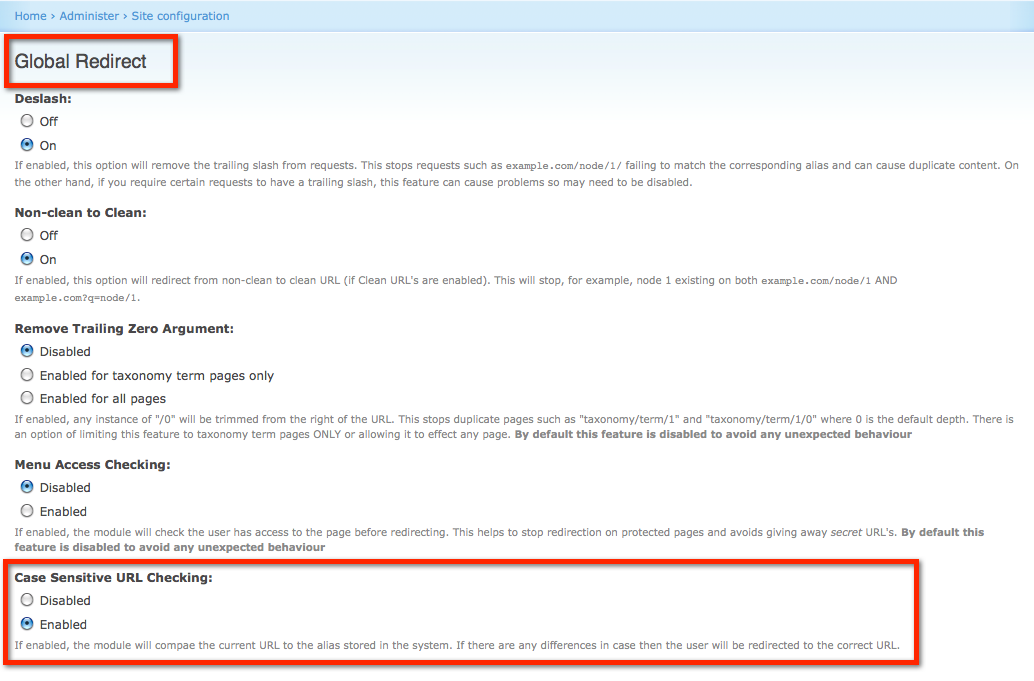
1. Global Redirect Module
One of the main module which comes bundled up in the Drupal SEO Checklist Module, and is highly recommended for Drupal SEO performance is the Global Redirect module. This prevents content from being displayed on multiple URLs when the path module is enabled. Displaying duplicate content at multiple URL’s can cause a loss for search engine site ranking. Thus, helping the websites with:
- Verification of the of current URLs and does 301 redirects to it if it is not being used.
- Verifies the current URL for trailing slash, removes it if they are present, and repeats check 1 with the new request.
- Verifies if the current URL is the same as the site front page and redirects to it if there is a match.
- Verifies if “clean URLs” feature is enabled and then checks whether the current URL is being accessed using the clean method.
- Verifies the access to the URL. If the user does not have an access to the path, then there are no redirects which are done.
2) PathAuto
Drupal provides the user with content friendly URLs with the help of PathAuto and automatically generates paths for various content. In simple words, it enables you to redirect from one path to another path or an external URL, utilizing any HTTP redirect status. This is significant if you want to replace the URL scheme for some reason and you don't want to break all existing links (search engines, user's bookmarks etc.) in other words, the Pathauto module automatically creates URL/path aliases for multiple kinds of content (nodes, taxonomy terms, users) without asking the user to manually specify the path alias.
It should be noted that multilingual URL alias support is still unstable and should be tested before use in production.
3) Intelligent Content Tools
Intelligent Content Tools module will assist you to personalize the content, and provides you with 3 functionalities:
1. Auto Tagging
2. Summary of text
3. Check Duplicate content
This module rectifies the plagiarised content and while the number of plagiarism checkers available in the market is high, the module notifies you if there is any duplicate content available on the website. It is an intelligent agent module based on Natural Language Processing. It’s a valuable tool for a website designer and content editor.
This should be taken into account that this project is not covered by the security advisory policy.
4) Taxonomy Unique
Taxonomy unique module prevents saving a taxonomy term. Meaning, when a term with the same name exists in the same vocabulary, the user can configure it individually for each vocabulary, and then can set custom error messages if a duplicate is found. It also provides the users with
An assurance that the term names are unique
- It is configured individually for vocabulary
- Set a custom error if the duplicates are found.
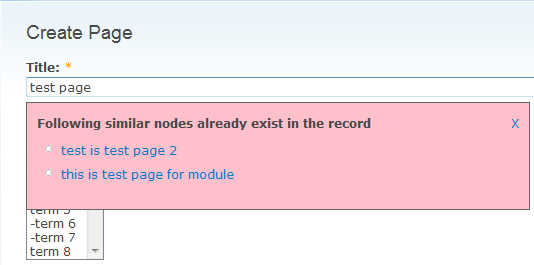
5) Suggest Similar Titles
Suggest Similar Titles module avoids the duplication of the titles for all types of content. This module matches with the node titles of same content type and advises you that one title is matching with this title which already exists in the database. This helps the admin/user to avoid duplication of content at the site. It also provides a setting page where the following settings can be made:-
Qualifying this feature for any content type
- The user can input ignore keywords in title comparison
- They can also select a maximum number of titles to show up as the suggestion
- Choosing whether this module should consider node permissions before displaying node title as a suggestion can be done.
- The user can input the percentage of how exactly the system should compare the title. For example, if you enter 75, then at least 75% matching title will be considered related
This module has template file to theme the suggested content as per requirement.
Conclusion
Yes, it is difficult and hard to construct a site that is 100 percent duplication free. The essential aspect is to make sure that no entire pages or a whole set of pages are duplicated from one site to the next.
But as we say - “Old habits die hard”, there can still be chances where you are indulged in this unfortunate act and this is when Drupal is your savior. At OpenSense Labs, we embrace the concept of duplicate free content. Contact us on [email protected] to learn more about the best ways to eliminate duplicate content.
Subscribe
Related Blogs
Drupal's Role as an MCP Server: A Practical Guide for Developers

"The MCP provides a universal open standard that allows AI models to access real-world data sources securely without custom…
What’s New in Drupal CMS 2.0: A Complete Overview

"Drupal CMS 2.0 marks a significant change in the construction of Drupal websites, integrating visual site building, AI…
Drupal AI Ecosystem Part 6: ECA Module & Its Integration with AI
Modern Drupal sites demand automation, consistency, and predictable workflows. With Drupal’s ECA module, these capabilities…




