Nothing is permanent as every cloud has a silver lining. People come and go in your life. Some may call themselves your neighbour, well-wisher or a even a friend. But only some leave an indelible imprint on your mind. These people continue to stay in your life either physically or even in your memories. The space of macro trends in technology is also a volatile one where one or the other tech marvel glows bright and others may see a downward spiral.
Webbmedia Group’s 2016 Trend Report says that the emerging technology breakthroughs are outpacing the evolution of public policies and discussions vis-à-vis ethics. It further states that our evolutionary responses to the technologies, that is pick-and-shovel for us to understand, is either to ignore them or to fear the worst. So, what does the macro trends in the tech industry look like in 2018?
Unwrapping macro trends
A macro trend refers to the pervasive and persistent directional shift of a certain phenomenon on a global scale. For instance, urbanisation, automation or the altering demographics are some of the examples of macro trends.
Macro trends help in zeroing in on the listicle consisting of all the things that would not fade away soon. Although they may attain a point where they are fully realised and are not considered trends but just the characteristics of technological fraternity.
Macro trends help in zeroing in on the listicle consisting of all the things that would not fade away soon
Longevity is usually seen as a significant characterisation of trends. Mega trends are the most pervasive and insistent phenomena. Megatrends, as defined by the Copenhagen Institute for Future Studies, are developing trends that help in predicting “the probable future - express what we know with great confidence about the future. Megatrends are certainties.” A phenomena like global warming come under the category of megatrends.
Right down at the end of the table are the fads - widespread but with a short spell lasting a few years or even less. Pokemon Go, an augmented reality game, reached unprecedented fame in 2016 but people are highly unlikely to be hunting down Pikachu in 2030.
Microtrends fall somewhere between fads and macro trends that are influential and last a few years. For instance, flexible workforce where a firm retains minimal staff and gets the work done mostly with external contracts is an example of micro trend. Inherent caveats to such microtrends, most often than not, become apparent in practice thereby leading to a trend in the opposite direction.
Macro trends in the tech industry
In an ever-evolving technological landscape, it is worth witnessing the macro trends in the tech industry to understand its progress and the path ahead.
Continuous Delivery
For superfast project deliveries, Continuous Delivery has been instrumental in handling software development. In addition to this, it has also been bearing fruit in enabling Evolutionary Architectures. Evolutionary Architecture is a terminology, created by ThoughtWorks, that stresses on supporting incremental, guided change as the first principle across various dimensions.
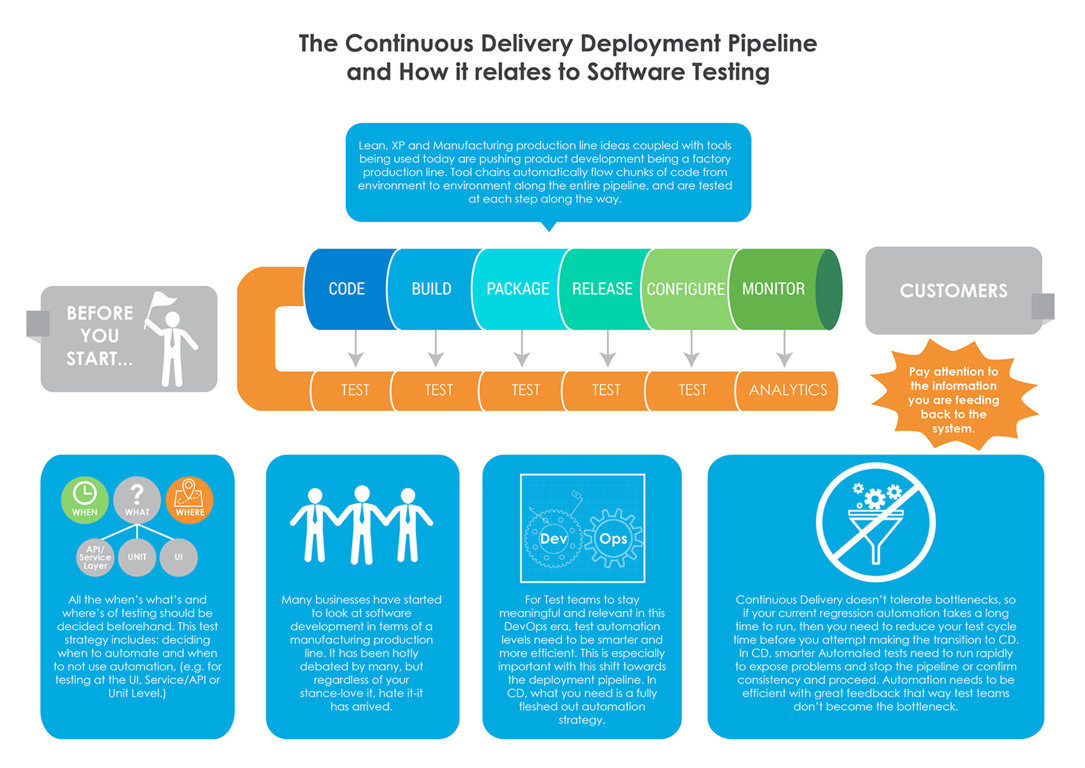
For superfast project deliveries, Continuous Delivery has been instrumental in handling software development.
With a cloud platform and nice automation techniques, software architecture can be treated as code - infrastructure, servers, interconnections, services, and networking that are defined and governed through version controlled text files. This helps in achieving architectural leaps that were never possible before.
Drupal factor in Continuous Delivery
Like the ship of Theseus, a thought experiment that questions whether a ship fundamentally remains the same object if its components are replaced, we can replace parts of our system until the entire thing is new. Thereafter, we can keep moving forward as necessary or strategic.
For instance, Drupal development can garner tremendous positives through agile development methodology. Agile manifesto was formulated in 2001 with the objective of implementing Continuous Delivery. The agile process uses an incremental and iterative approach to govern project development.
Service NSW portal is an initiative established by the NSW Premier for offering a centralised point of transaction for the Australian citizens with government agencies. In combination with Agile methodology, the Drupal development of the portal was completed within the stipulated timeline of 6 months that was agreed upon before the project started.
Microservices
Microservices architecture style constitutes a collection of small, autonomous services where each of the services itself-contained and implements a single business capability.
Microservices has been a buzzword in the recent years among the web chefs as it comes up with a whole lot of benefits:
- Autonomous deployments: Update a service without redeploying the complete application and rollback or roll forward an update during mishaps. Fixing bugs and feature releases are more manageable with fewer challenges.
- Autonomous development: Building, testing and deploying a service would require a single development team which leads to continuous innovation and faster release cadence.
- Small teams: Teams can lay their emphasis onto one service thereby streamlining the understanding of the codebase with the smaller scope for each service.
- Isolation of faults: Downtime in one of the services won’t affect the entire application which does not mean that you get resiliency for free.
- Tech stack mixture: Technology that is deemed most suitable for a service can be chosen by the teams.
- Scalability at granular levels: Independent scaling of services is possible.
It does have a set of caveats that are needed to be considered like:
- Intricacy: More moving parts are there in microservice application than the equivalent monolithic application.
- Development and testing: Developing against service dependencies would need a different approach and testing service dependencies is challenging particularly when the application is evolving rapidly.
- Dearth of administration: The decentralised approach to building microservices may result in so many different languages and frameworks making it harder to govern.
- Network congestion and latency: Usage of granular services can lead to more interservice communication and if the chain of service dependencies gets too elongated, additional latency can be an issue.
- Data integrity: Data consistency can be an issue with each microservice responsible for its own data persistence.
- Governance: Correlated logging across services can become an arduous task.
- Update issues: If not for a careful design, several services updating at a given time could lead to backward or forward compatibility.
- Team skill-set: As the highly distributed systems, microservices need to have a team with the right skills and experience.
Apparently, microservices have a great potential but it has to cover a long journey still. Businesses would find it a formidable task to migrate from a monolith to microservices. It is difficult to decide when to split services as it needs a good underlying platform and wonderful DevOps practices.
Drupal factor in microservices
A presentation held at DrupalCon Vienna 2017 showed an awesome and easy way of integrating Drupal 8 in a microservices architecture. With Symfony components, Composer to govern external dependencies and astounding results of the WSCCI initiative, Drupal 8 proved to a useful content store.
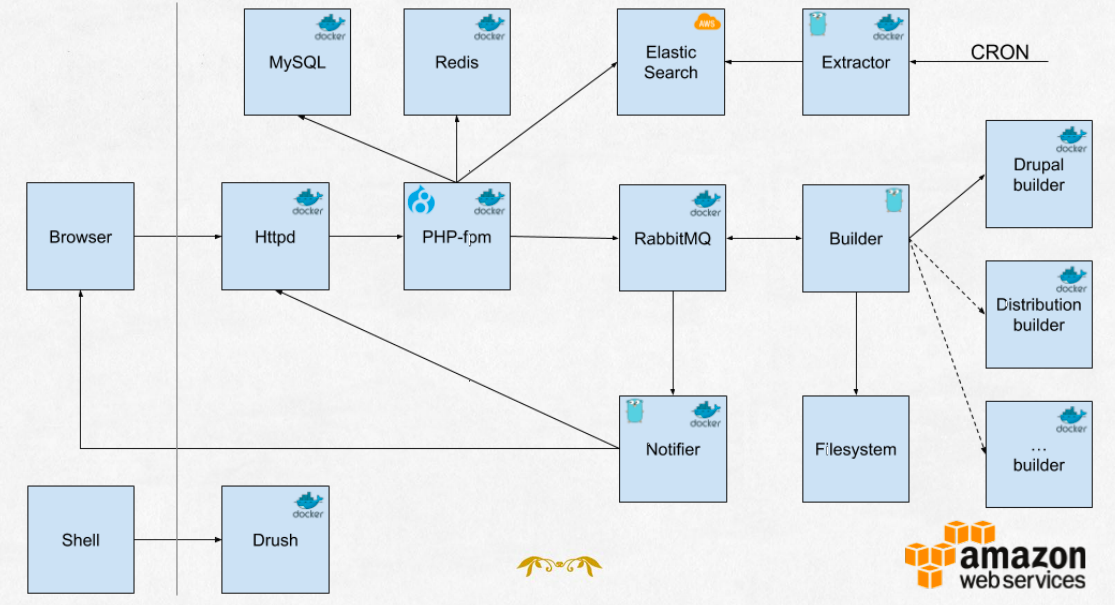
It demonstrated the delegation of asynchronous work from Drupal to a bunch of very reactive applications written in Go with the help of some RabbitMq queues. Elasticsearch was used as a common data storage between services and REST endpoints were exposed where the external services could notificate back to Drupal.
Moreover, methods of connecting websocket server to push and pull messages between services were displayed and Ansible and Docker were used for running all these services in a controlled and replicable manner.
Machine Learning
Machine learning, a method of data analysis for automating analytical model building, is a branch of artificial intelligence. It is based on the notion that systems can learn from data, identify patterns and take part in decision-making with minimal human intervention.
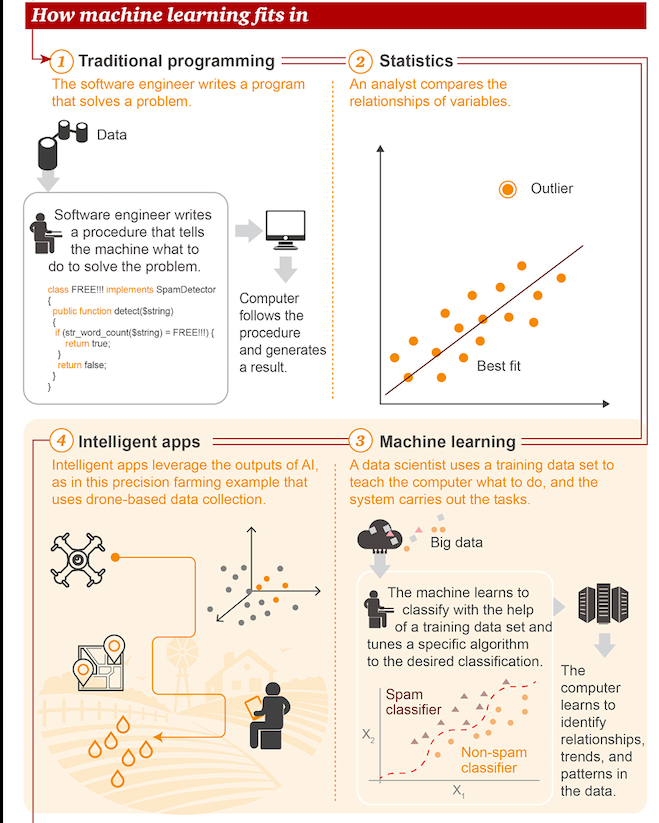
Towards the path of productivity
Machine learning is on a roll with astronomical metamorphosis in the Gartner Hype Cycle, down the “peak of inflated expectations” through the “trough of disillusionment” to the “plateau of productivity”.
Business enterprises are beginning to consolidate all the different proofs of concept that has popped over in the recent years. With tools, platforms and services on one side and inflated expectations propagated by media and artificial intelligence (AI) on the other side infiltrating market, several questions are being pondered over. How can AI benefit an organisation? What skills does an in-house team need? What software, tools and platforms would be the right fit for a business? These are the right set of questions to move forward in the direction of the “plateau of productivity”.
Machine learning is on a roll with astronomical metamorphosis in the Gartner Hype Cycle
An intelligent approach to development
With hyper-advancement of machine learning, curiosity ignites interesting question - How will it affect the job of software developers who have always written explicit instructions for computers, though, at accentuating levels of abstraction?
It is too soon to tell. There have been a superabundance of attempts at higher order languages where human developers just have to elaborate their intent and an ML/AI system conjures up implementation code. Although not far-fetched but these techniques are a long way-off.
Interestingly, hurdles plaguing other technologies may be improved with the help of ML. For instance, take a look at architecture review for an existing suite of enterprise systems. There might be highly intricate interactions between systems and components, sophisticated data access patterns and relationships etc.
Instrumenting these systems and then applying ML would provide better insight to do enterprise architecture in an improved way. Insights like “apply the strangler pattern here”, “couple these two related systems”, “remove this flaky old system” etc. can prove to be a smart way of business development.
Drupal factor in machine learning
So, how can you personalise web content experiences on the basis of subtle elements of a person’s digital persona? Standard personalisation mechanisms point to content which is based on a user profile or behavioural patterns.
Deep-Feeling, a proof-of-concept project, uses machine learning techniques to provide improved content recommendations to users. A presentation in Drupalcon Baltimore 2017 used the Instagram API to access a person’s stream-of-consciousness and filtered their feeds through a computer-vision API. This was used to detect and learn subtle themes about the user’s preferences.
The presentation focussed on establishing an idea about the sort of experiences that the user deems fit to be worth sharing. It was, then, used to match the user’s characteristics against their own databases. In this proof-of-concept, they used Acquia Lift service and Drupal 8 to recommend travel experiences on the basis of sort of things that a person shares.
On the Cloud
AWS defines cloud computing as “the on-demand delivery of compute power, database storage, applications, and other IT resources through a cloud services platform via the internet with pay-as-you-go pricing”.

Complications in Cloud
Today, more than ever before, cloud is much more complicated than an edict from the Chief Technology Officer to “put everything in the cloud”. With AWS featuring so heavily, is that an indication of its maturity? Or is that the resultant of Amazon’s explicit strategy to out-compete other cloud platforms based on features? It’s a mix of both but many retail enterprises are dodging AWS as they see Amazon as a competitor and have started following a strategic decision-making as to forbid using their services.
Today, more than ever before, cloud is much more complicated than an edict from the Chief Technology Officer to “put everything in the cloud”.
There is a discernible growth in confidence in Azure and Google Cloud platform with both maturing as platforms and their messaging having a firm resonance with the buyers. There is a plenitude of choice in cloud but with new data protection laws such as the EU’s GDPR coming into play, it has complicated the situation. Organisations are finding it difficult to identify which cloud will support their regulatory and compliance obligations.
Feature parity
Another trend that can be witnessed is the use of feature parity as an objective while performing a cloud migration, product redevelopment or legacy system upgrade. It is hardly a good idea to simply reimplement a 10 or 15 year old system - bugs and all - using latest technology.
Often the excuse tends to be that “we do not want to confuse the business”. Or, there are concerns about changing the process or calculations but the output is, most often than not, a long, sluggish, big-bang delivery with superabundance of risk. Stakeholders are often not happy with a project that is late, exceeds budget, and does not deliver anything new for the business.
Instead, thought leaders in the IT should be more eager to raise question on whether the logic written more than a decade ago is a right fit for today’s business workflow. Also, they should provide their users more credit for being able to absorb a new and overall more capable system. Organisations should be closely examining the features that they really need rather than recreating a complete feature-set on a new platform.
Betterment in platform-thinking
There is a wave of ‘platform-thinking’ doing rounds which is basically deliberate encapsulation of useful capabilities and business functions into self-service, reusable platform components. As the technology and business platforms gains new features, it enables the business enterprises to speed up time-to-value.
The rise of platforms is becoming a significant latest trend. Whether it is public platform like AWS and Azure or the private ones like Cloud Foundry and Kubernetes, Cloud has given organisations new options for infrastructure deployment.
Container management
Google Cloud states that “containers offer a logical packaging mechanism in which applications can be abstracted from the environment in which they actually run”.
The containerisation trend has been creating an ecosystem where all of our tools now work with containers. And in some ways, containers, are the new POSIX, the latest universal interface. Other significant trends like microservices, evolutionary architecture, cloud-by-default work tremendously well with containers.
Not long ago, big players in the industry were engrossed in the conversation involving topics of GIFEE - Google’s Infrastructure For Everyone Else. Kubernetes is just a Google-style infrastructure that can be leveraged by everyone. Google pushed hard and put in a lot of resources with the objective of getting people onto the Google cloud offering. Eventually, Kubernetes became the default container platform. Kubernetes is an open source container orchestration system for automation of deployment process and scaling and governance of containerised applications.
Moreover, Kubernetes has been becoming more accessible to run at scale. Running resilient, production clusters is becoming easier with improvements in the core Kubernetes software. In addition to this, Kubernetes is coming up with better tooling and highly active ecosystem. Most of the big cloud providers have started offering Kubernetes-based hosting.
Virtualisation
When the VMware virtual machines came into the scene in 1999, it was a slight hint towards virtualisation long-term impact on revolutionising all aspects of software. Virtual machines are used in everything ranging from developer workstations to Google-sized data centres. Docker, Kubernetes and all those today’s super exciting cloud technologies are the resultant of virtualisation.
The Drupal factor in Kubernetes
At a conference held in the Great Indian Developer Summit Bangalore 2018, a demonstration showed the orchestration, powered by Kubernetes, that provides a simple way to leverage the scalability and power of Drupal.
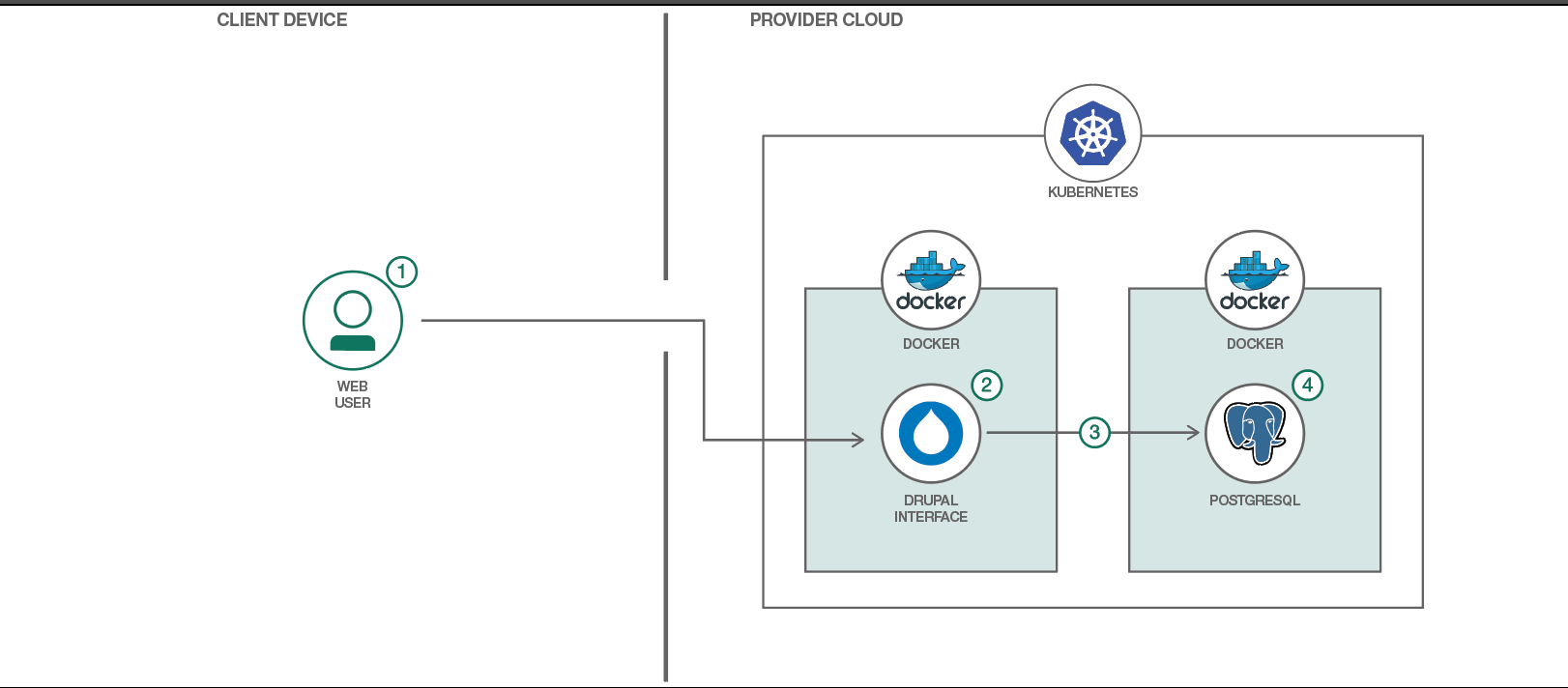
A Drupal site was set up using Kubernetes and Postgres by splitting the services into containers. It involved:
- Configuring an app that ran multiple containers in Kubernetes
- Running a website hosted via Kubernetes
- Using Kubernetes-persistent volumes to govern Drupal configuration between container restarts.
- User interactions with the Drupal web interface
- Drupal container using its persistent volume to store website date but not content
- PostgreSQL container using persistent volume to store the database contents.
Data streaming
The world is expecting real-time analytics. It is a de-facto thing that we have to accommodate as we design systems. We savour the merits yielded from an event-based streaming architecture like loose coupling, high performance, autonomous components and scalability. But the need for streaming has been driven by the analytics requirement, that means, you just cannot meet this need without streaming.
Maturity in event-driven architecture is associated with rapid rise in data streaming. These systems are now a run-of-the-mill thing and well understood. Also, new techniques like using streams as persistent storage of enterprise facts are seeing a steady rise. Streaming is here to stay!
Blockchain
Forbes defines Blockchain as “a public register in which transactions between two users belonging to the same network are stored in a secure, verifiable and permanent way. The data relating to the exchanges are saved inside cryptographic blocks, connected in a hierarchical manner to each other. This creates an endless chain of data blocks -- hence the name blockchain -- that allows you to trace and verify all the transactions you have ever made.”
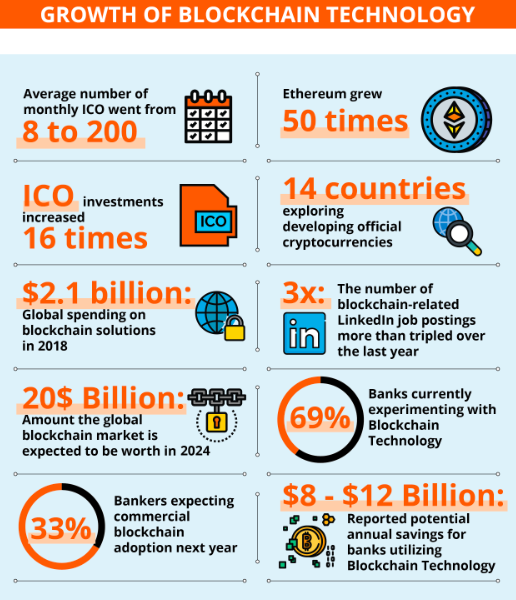
This technology holds the promise to alter industries. Even though the conversation is often surrounding financial opportunities, it has lot more to offer in government, healthcare, supply chain, content distribution and many more. However, many blockchain technologies are still immature and unproven which needs to be unregulated.
Blockchain technology holds the promise to alter industries
Pragmatic approach to blockchain requires a clear understanding of the business opportunity, immense capabilities and the caveats, a trust architecture and the necessary implementation skills. Before kickstarting a distributed-ledger project, your team should have the cryptographic skills to understand the possibilities. Identify the integration points with existing infrastructures in addition to monitoring the platform evolution and its maturation. Be very cautious while interacting with vendors.
Today, Ethereum smart contracts and the Corda distributed ledger are praiseworthy options to consider.
The Drupal factor in Blockchain
Chainfrog has been working on blockchain technology since its early stages. They exhibited a use case where user data like communication history, addresses or the profile data will be available to users in a big enterprise.

Rather than making an HTTP call everytime a new user is added, Chainfrog proposed to remove the middleman, in this case, API, and adopt a peer-to-peer immutable ledger.
Whenever a new user would be added to the Drupal system, Chainfrog’s blockchain based solution ‘Blockbinder’ will help in recording everything in a data table. This , thereby, ensures that all the Drupal installations inside a firm would synchronise their user data within 30 seconds of any new addition in one of their installations.
Conversational platforms
Conversational UI and Natural Language Processing (NLP) are often in the scheme of things when it comes to recent innovations in the tech industry. The foundational example is the Amazon Echo.

For designing a device with no screen, Amazon started considering the development of conversational UI. Carrying on a conversation with a device or chatbot is not anymore reserved for the likes of Alexa, Cortana or Siri. With the help of APIs and third-party services to do the heavy lifting, these capabilities could be leveraged by device makers and enterprise developers.
Conversational platforms are driving a paradigm shift in which the burden of translating intent shifts from user to computer.
The Drupal factor in conversational platforms
Chatbot API, a Drupal module, can be leveraged to integrate a bot in the site. It is an extra layer that falls between your Drupal installation, NLP and various chatbots and personal assistants. It can work with systems like Dialogflow, Alexa, Cisco Spark Microsoft and Twilio.
Immersive Experience
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are moving towards the mainstream adoption. Businesses showing interests in VR beyond gaming and also novel applications of AR to improve productivity. The technology is still developing and needs specific skills such as 3D modelling but organisations are preparing itself for this new wave of interaction.
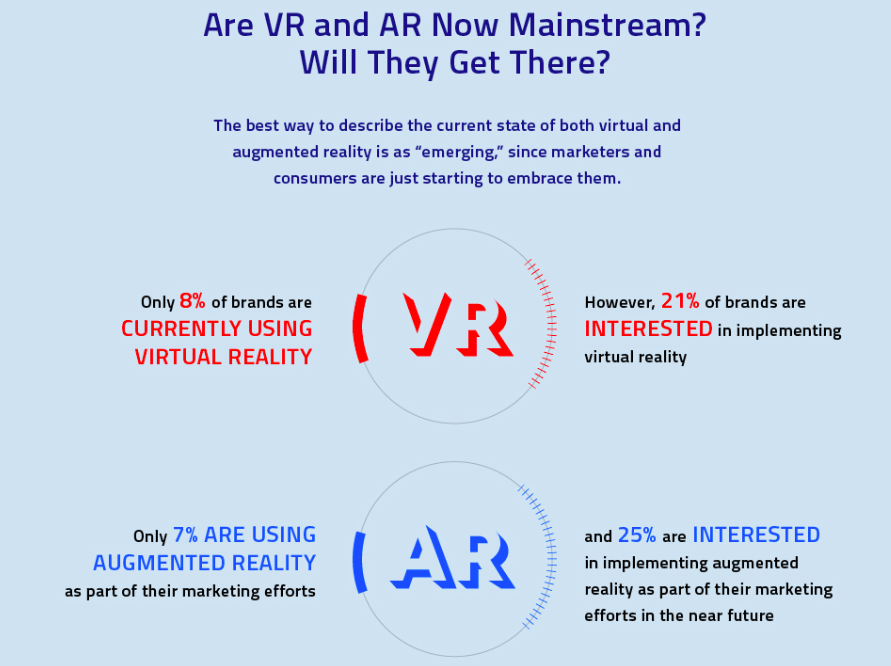
In the near future, VR and AR will be mainstream capabilities that businesses need to build, buy or rent. VR and AR would allow natural interactions between people and the digital world.
The Drupal factor in Immersive experiences
The demonstration shown in the video depicts a shopper interacting with the AR application. The mobile application of Freshland Market (a fictional grocery store), built on Drupal 8, guided the shopper through the lists while shopping.
Another demonstration shows a decoupled React VR application on top of Drupal 8. The Drupal site of Massachusetts State University (a fictional university) stores all the content and the media that is going to be featured in the VR tour.
Internet of things and Digital Twins
Internet of things (IoT) has been revolutionising the way we see connected world. Basically everything we see around us can be connected through internet. Almost!
One of the key trends in the IoT in the recent years is the digital twins. Forbes defines it as “a virtual model of a process, product or service. This pairing of the virtual and physical worlds allows analysis of data and monitoring of systems to head off problems before they even occur, prevent downtime, develop new opportunities and even plan for the future by using simulations”.
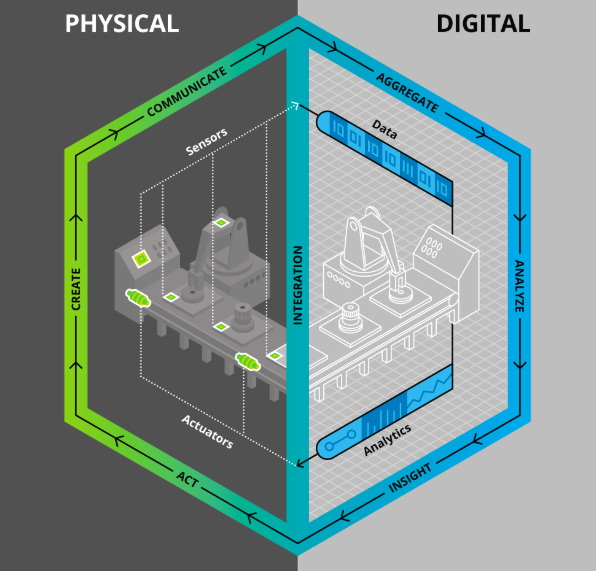
John Vickers, NASA’s leading manufacturing expert and manager of NASA’s National Centre for Advanced Manufacturing says that “the ultimate vision for the digital twin is to create, test and build our equipment in a virtual environment”.
For instance, GE’s digital wind farm paved new ways of improving productivity. GE uses the digital environment to inform the configuration of each wind turbine before the construction commences. Its aim is to generate 20% gains in efficiency by assessing the data from each turbine that is fed to its virtual equivalent.
The Drupal factor in IoT
A session held at DrupalCon New Orleans 2016 showed how Drupal and internet of things and come together. It showed a demonstration that used a barometric pressure sensing, GPS-enabled wearable armband connected to the internet. It could, then, display an icon to provide the weather forecast for the current location.
Conclusion
While the planet Earth keeps on revolving around the sun, not only the climate and year changes with that but the people and their needs as well. And so happens technological innovations and, thus, macro trends listicle go on adding and subtracting the name of technologies every few years.
The macro trends in technology shown in this blog post are the key mentions that are being witnessed in recent times and will continue growing. Drupal, as a stupendous content store, keeps scaling itself with a robust community presence that makes it relevant and useful in the times of tech innovations.
We, at Opensense Labs, keep following our everlasting approach towards keeping pace with new inventions. We can give your business a digital transformation that it deserves with the help of our experts who have years of experience in Drupal development.
Contact us at [email protected] to develop Drupal-based projects using such futuristic technologies that are doing rounds in the macro trends.
Subscribe
Related Blogs
Drupal's Role as an MCP Server: A Practical Guide for Developers

"The MCP provides a universal open standard that allows AI models to access real-world data sources securely without custom…
What’s New in Drupal CMS 2.0: A Complete Overview

"Drupal CMS 2.0 marks a significant change in the construction of Drupal websites, integrating visual site building, AI…
Drupal AI Ecosystem Part 6: ECA Module & Its Integration with AI
Modern Drupal sites demand automation, consistency, and predictable workflows. With Drupal’s ECA module, these capabilities…




