More and more users want the content to be available via a host of different devices. Various new interfaces and devices are thronging the technology landscape and are touted to bring about sweeping changes. There are even talks of website-less future. Smart wearables, Internet of Things, conversational user interface etc. have been gaining traction and are changing the way we experience the internet. New web-enabled devices need the content that the websites do but in a different format which creates complications in the way we develop. Disseminating content can have different needs from one setup to another.

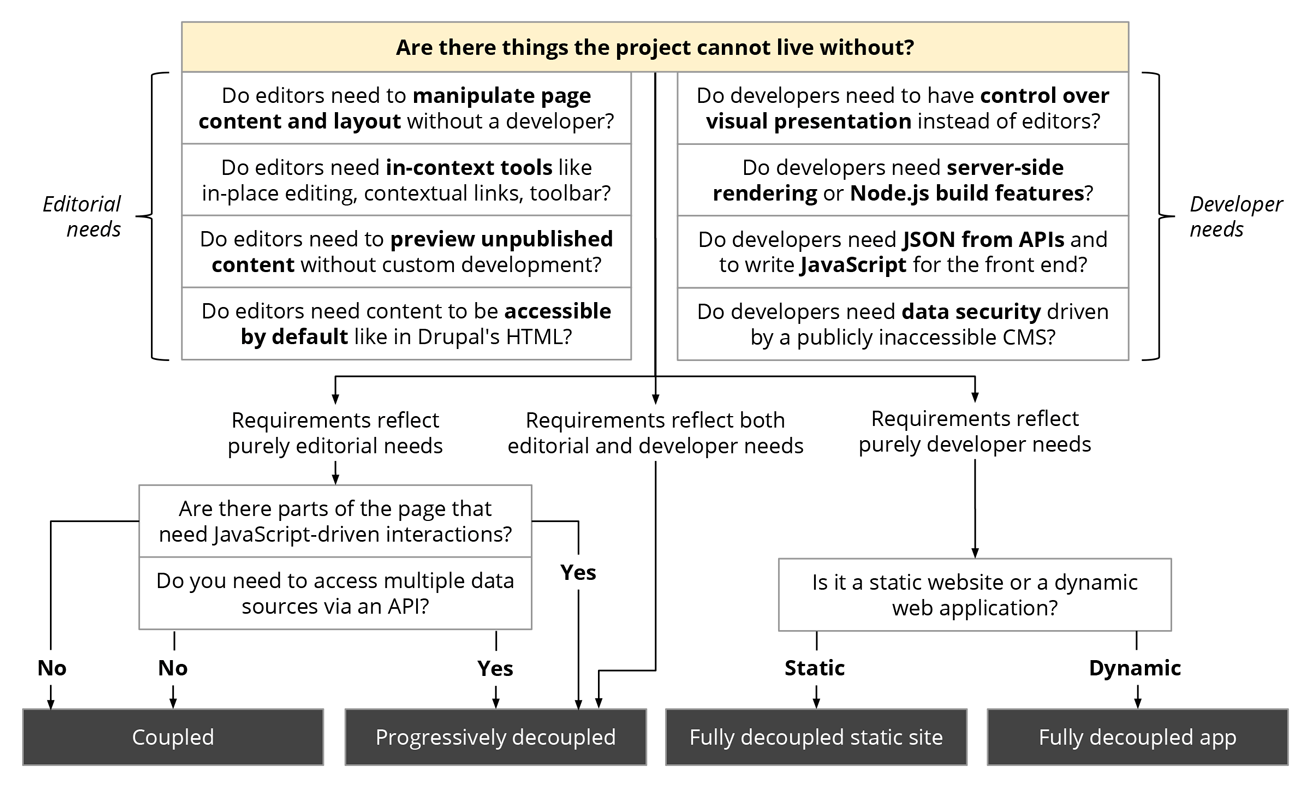
The content management system (CMS) is rife with labels such as ‘decoupled’ and ‘hybrid’ which requires to be dissected for a better understanding of their benefits. Decoupling the backend of a content management system (CMS) from the frontend can be a remarkable solution for a lot of issues that are caused when you move away from standard website-only deliveries. Decoupling the CMS streamlines the process of republishing the content across numerous channels ranging from websites to applications. Decoupled CMS is not new, but as the digital arena observes changes, it gets more and more important.
The Drupal Connect
As one of the leaders in the CMS market, Drupal’s content as a service approach enables you to get out of the page-based mentality. It gives you the flexibility to separate the content management from the content display and allows the front-end developers to build engrossing customer experiences.
Decoupled Drupal implementations are becoming ubiquitous due to its immense capability in giving a push to digital innovation
Decoupled Drupal implementations, which involves a full separation of concerns between the structure of your content and its presentation, are becoming ubiquitous due to Drupal’s immense capability in giving a push to digital innovation and being a great solution in adopting novel approaches.
Drupal Community has been working on a plenitude of API-first architectures by utilising its core REST, JSON:API and GraphQL features. But there are alternative solutions, too, available in decoupled Drupal ecosystem that can be of great significance. Let’s explore them:
RESTful Web Services and others
While RESTful Web services module helps in exposing entities and other resources as RESTful web API and is one of the most important modules when it comes to decoupled Drupal implementation, there are several others that can come handy as well.
Implementing the Apache CouchDB specification and focussing upon content staging use cases as part of the Drupal Deploy ecosystem, RELAXed Web Services module can be of immense help. The CouchDB helps in storing data within JSON documents that are exposed via a RESTful API and unlike Drupal’s core REST API, it enables not just GET, POST, DELETE but also PUT and COPY.
There’s a REST UI module that offers a user interface (UI) for the configuration of Drupal 8’s REST module. You can utilise Webform REST module that helps in retrieving and submitting webforms via REST. For protracting core’s REST Export views display in order to automatically converting any JSON string field to JSON in the output, REST Export Nested module can be useful. By offering a REST endpoint, REST menu items module can be helpful in retrieving menu items on the basis of menu name. And when you need to use REST for resetting the password, REST Password Request module can be helpful. It is worth noting that Webform REST, REST Export Nested and REST Password Request are not covered by Drupal’s security advisory policy but are really valuable.
JSON:API and others
JSON: API module is an essential tool when you are considering to format your JSON responses and is one of the most sought after options in decoupled Drupal implementations. But there is, again, plenty of options for availing more features and functionalities.
When in need of overriding the defaults that are preconfigured upon the installation of JSON: API module, you can leverage JSON: API Extras. By offering interfaces to override default settings and registering new ones that the resultant API need to follow, JSON: API Extras can be hugely advantageous in aliasing resource names and paths, modifying field output via field enhancers, aliasing field names and so on. And for the websites that expose consumer-facing APIs through REST, JSON: API or something similar, Key auth module offers simple key-based authentication to every user.
For streamlined ingestion of content by other applications, Lightning API module gives you a standard API with authentication and authorisation and utilises JSON: API and OAuth2 standards through JSON API and Simple Oauth modules.
GraphQL and others
GraphQL module is great for exposing Drupal entities to your GraphQL client applications. There are some more useful modules based on GraphQL. To enable integration between GraphQL and Search API modules, there is a GraphQL Search API module. Injecting data into Twig templates by just adding a GraphQL query can be done with GraphQL Twig module. To expose Drupal content entity definitions through GraphQL via GraphQL Drupal module and develop forms or views for entities via front-end automatically, you have GraphQL Entity Definitions module.
OpenAPI and related modules
OpenAPI describes RESTful web services on the basis of the schema. There is OpenAPI module in Drupal, which is not covered by Drupal’s security advisory policies but can integrate well with both core REST and JSON: API for documentation of available entity routes in those services. And for implementing an API to display OpenAPI specifications inside a Drupal website, you get OpenAPI UI module. And ReDoc for OpenAPI UI module offers the ReDoc library, which is an Open API/ Swagger-generated API reference documentation, for displaying Open API specifications inside Drupal website. Then there is Swagger UI for OpenAPI UI module that gives you Swagger UI library in order to display OpenAPI specifications inside Drupal site. You can also utilise Schemata module that provides schemas for facilitating generated documentation and generated code.
Contentajs and related modules
The need for a Nodes.js proxy that acts as middleware between Drupal content API layer and Javascript application can be addressed with the help of Contenta.js. For Contenta.js to function properly, Contenta JS Drupal module is needed. This module is part of the Contenta CMS Drupal distribution. The Node.js proxy is essential for decoupled Drupal because of data aggregation, server-side rendering and caching. Contenta.js constitutes multithreaded Node.js server, a Subrequests server for the facilitation of request aggregation, a Redis integration and simple approach to CORS (Cross-origin resource sharing).
There are several effective modules that are part of the Contenta CMS decoupled distribution and integrates perfectly with Contenta.js. You have Subrequest module that tells the system to execute multiple requests in a single bootstrap and then return everything. JSON-RPC module offers a lightweight protocol for remote procedure calls and serves as a canonical foundation for Drupal administrative actions that are relied upon more than just REST. To resolve path aliases, Decoupled Router module gives you an endpoint and redirects for entity relates routes.
In order to enable decoupled Drupal implementations to have variations on the basis of consumer who is making the request, you can use Consumers module. You can use Consumer Image Styles that integrates well with JSON: API for giving image styles to your images in the decoupled Drupal project. And there is Simple OAuth module for implementing OAuth 2.0 Authorisation Framework RFC.
Of relating to JavaScript frameworks
Decoupled Blocks module is great for progressive decoupling and enables front-end developers to write custom blocks in whatever javascript framework that they prefer to work on. If you want to implement using Vue.js, you can use Decoupled Blocks: Vuejs. It should be noted that both of these are not covered by Drupal’s security advisory policies.
React Comments comes as a drop-in replacement for the Drupal core comment module frontend.
Also, there is a jDrupal module, which is a JavaScript library and API for Drupal REST and can be leveraged for Drupal 8 application development.
Conclusion
With Drupal as the decoupled web content management, developers can get to use a plentitude of technologies to render the front end experience.
RESTful web services, GraphQL and JSON: API are not the only resources that you get in the decoupled Drupal ecosystem. In fact, there are plenty of other alternatives that can be of paramount importance.
Drupal development is our forte and bringing stupendous digital experience to our partners has been our prime objective. Contact us at [email protected] and let us know how you want us to be a part of your digital transformation goals.
Subscribe
Related Blogs
Drupal's Role as an MCP Server: A Practical Guide for Developers

"The MCP provides a universal open standard that allows AI models to access real-world data sources securely without custom…
What’s New in Drupal CMS 2.0: A Complete Overview

"Drupal CMS 2.0 marks a significant change in the construction of Drupal websites, integrating visual site building, AI…
Drupal AI Ecosystem Part 6: ECA Module & Its Integration with AI
Modern Drupal sites demand automation, consistency, and predictable workflows. With Drupal’s ECA module, these capabilities…




